Master and PhD Work
2018
Mr. Suporn Kittivinitchnun

Dissertation Title: Utilization of Biomass-Based Reducing Agent for Sustainable Iron
and Steelmaking Process
Degree: D.Eng
Publication: S. Kittivinitchnun, A. Tawai, T. Threrujirapapong, U. W. Hartley, P. Kowitwarangkul, A Review of Biomass-Based Reducing Agent Utilization for Sustainable Iron and Steelmaking Process, Proceedings of the 2nd Materials Research Society of Thailand International Conference (MRS-Thailand 2019), Pattaya, Thailand, July 10-12, 2019, pp.60-80.
Abstract: Since iron and steelmaking industry is one of the most intensive fossil carbonaceous material consumptions which have a direct impact on CO2 emission, it is therefore significantly important to decrease these consumptions. Several kinds of biomass could be applied as a reducing agent and fuel to replace coal and coke in iron and steelmaking process. The aim of this review work is to investigate the importance of biomass which is carbon neutral resource in the sustainable development of the iron and steelmaking process. The review carried out an exploration of biomassbased products as alternative reducing agents and the possibilities of biomass use in iron and steelmaking processes. The paper also puts forward relevant theories of iron and steelmaking. Finally, the development of biomass-based reducing agents for future research was discussed.
Mr. Patiparn Ninpetch

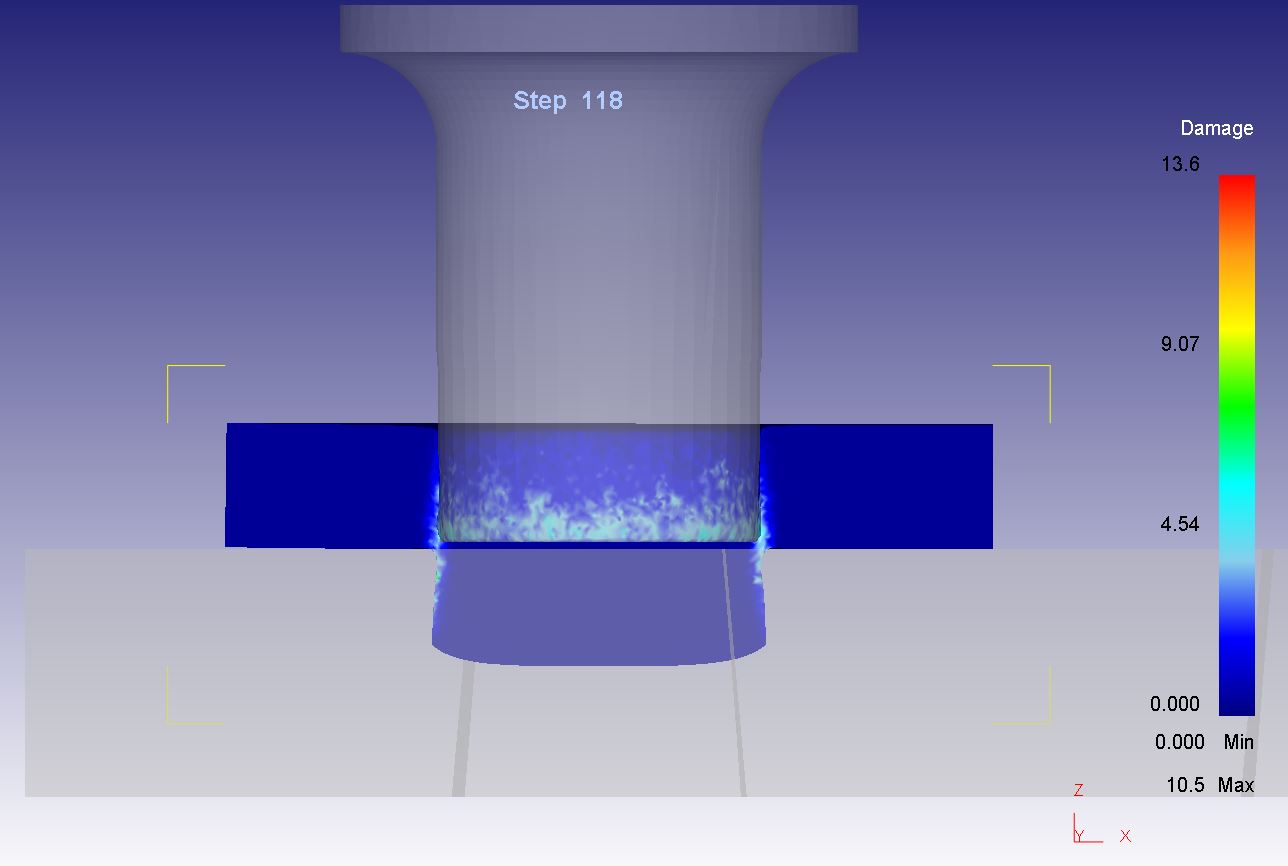
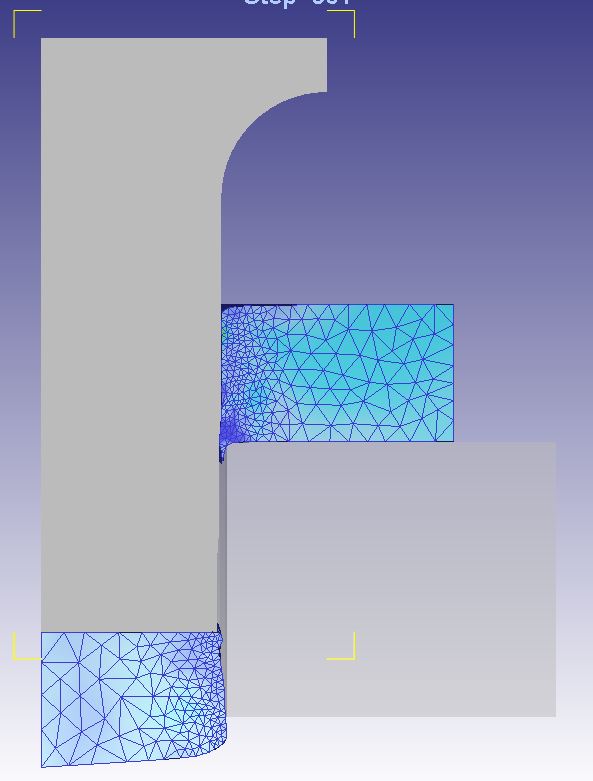
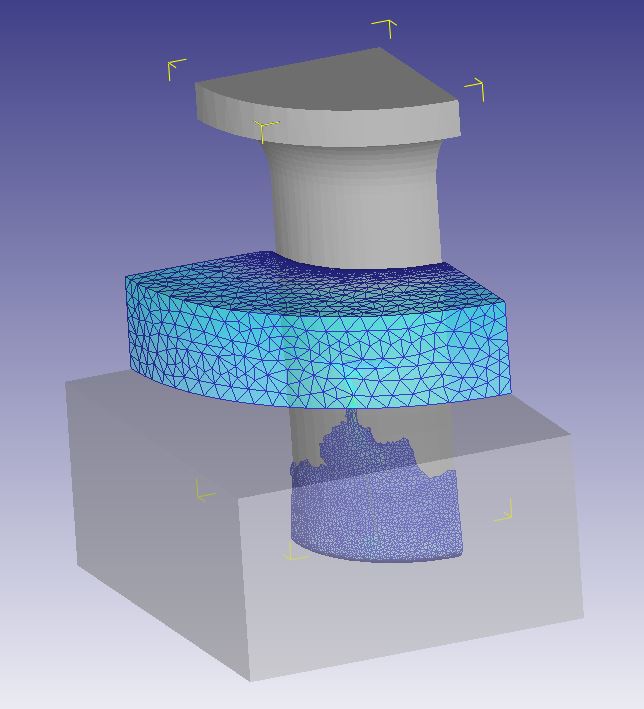
Dissertation Title: Computational Investigation and Modelling on Metal 3D Printing Process of Medical Materials for Implantable Medical Device Applications
Degree: D.Eng
Publication: Effect of Scanning Strategies and Pre-Heating on Distortion in Selective Laser Melting using Numerical Modelling
Abstract: Selective laser melting (SLM) process is an emerging manufacturing technology for producing the metallic parts with complex geometries. SLM process has extensive applications including automotive parts, aerospace parts, and medical parts, etc. However, the distortion of parts during the fabrication process is still a significant problem to overcome. The distortion in SLM process can occur due to the thermal history of the built layers and thermal gradient from rapid heating and cooling. In this research, the effect of scanning strategies and preheating on distortion in selective laser melting process of AlSi10Mg alloys were investigated through numerical modelling. The numerical simulation was performed using the commercial software Simufact Additive 2020. The cantilever beam was used as specimens for this study. The laser power, scanning speed, layer thickness, hatch spacing, laser spot size applied for this research were 300 W, 1,000 mm/s, 30 µm, 100 µm, 70 µm, respectively. It was discovered that the numerical modelling result is in good agreement with the experiment result. The distortion of parts can be mitigated with the low temperature gradient occurred during the fabrication process. The part distortion is also reduced when the substrate plate is heated during the process. The findings from this research will be useful for further research studies to reduce and eliminate the parts distortion.

2017
Ms. Kornrawee Munpakdee

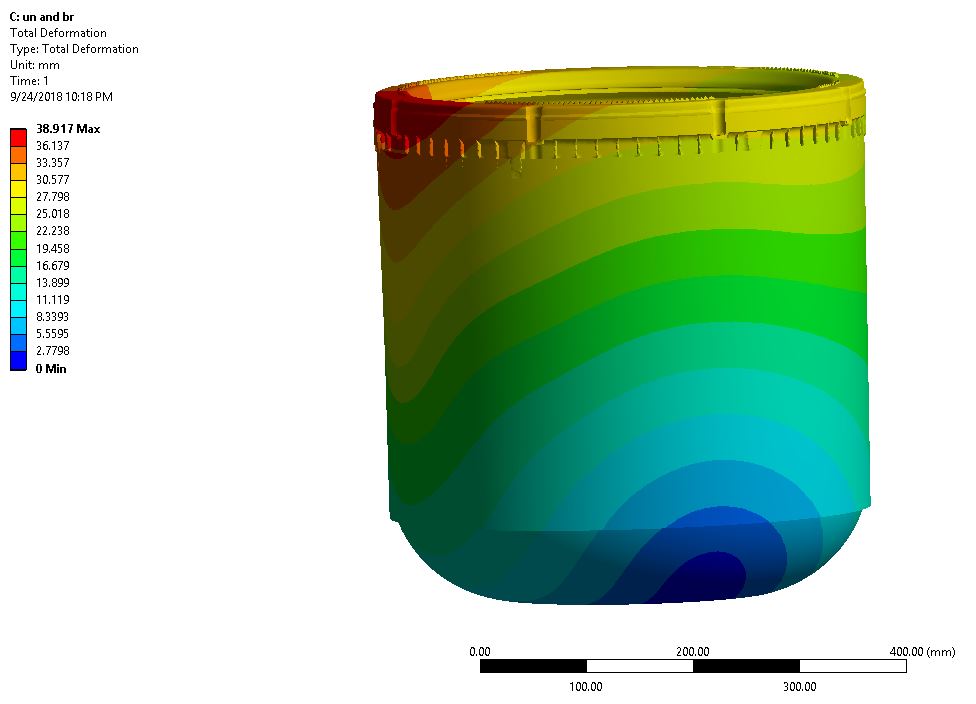
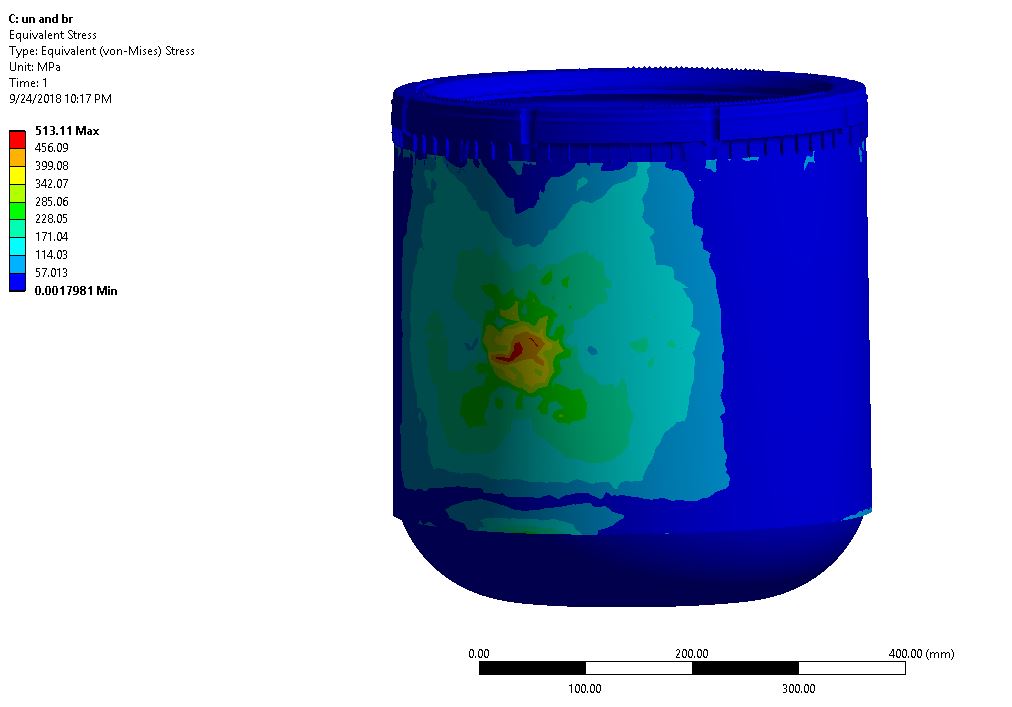
Thesis Title: Prediction of Porosity Defects in Precious Metal Casting by using Computer Simulation
Degree: M.Eng
Publication: Effect of Casting Parameters on Porosity Defects in Platinum 950 Centrifugal Investment Casting via Numerical Modelling
Abstract: In jewelry manufacturing industry, the casting defects such as shrinkage porosity and gas porosity are major concerns that cause the loss in productivity and increase production cost. The pouring temperature and sprue design are important casting parameters that affect on porosity formation. The aim of this work is to study the effects of these parameters on shrinkage porosity defects in the centrifugal investment casting process with vacuum atmosphere. The simulation software, FLOW-3D CAST, was used in this study. The prediction of shrinkage porosity was carried out based on the Niyama criterion. The platinum alloy Pt950Ru which has composition of 95% Platinum and 5% Ruthenium alloy was used as a raw material in this study. The simulation results were validated with the experimental results from the example factory, Christy Gem Co., Ltd. The results show that the shrinkage porosity with the casting temperature of 1980 oC is more than that of 1950 oC. From the cross section of the specimen, it was found that the ring with sprue diameter of 2 mm has more porosity area than the other with diameter of 4 mm approximately 0.5% compared to the total area. The simulation result reveals that the sprue designs with larger diameter can contain high temperature for a longer period of time and provide better feeding during solidification. The results obtained from this research could contribute to the improvement of jewelry casting process in the future.
[1] K. Munpakdee, P. Ninpetch, S. Otarawanna and P. Kowitwarangkul, Prediction of Porosity Defects in Platinum 950 Centrifugal Investment Casting, Oral presenation, Proc. of the 2nd MRS Thailand International Conference, 10-12 July 2019, The Zign Hotel, Pattaya, Thailand, Abstract SYM11_O12

Mr. Kritsanapong Boonpen

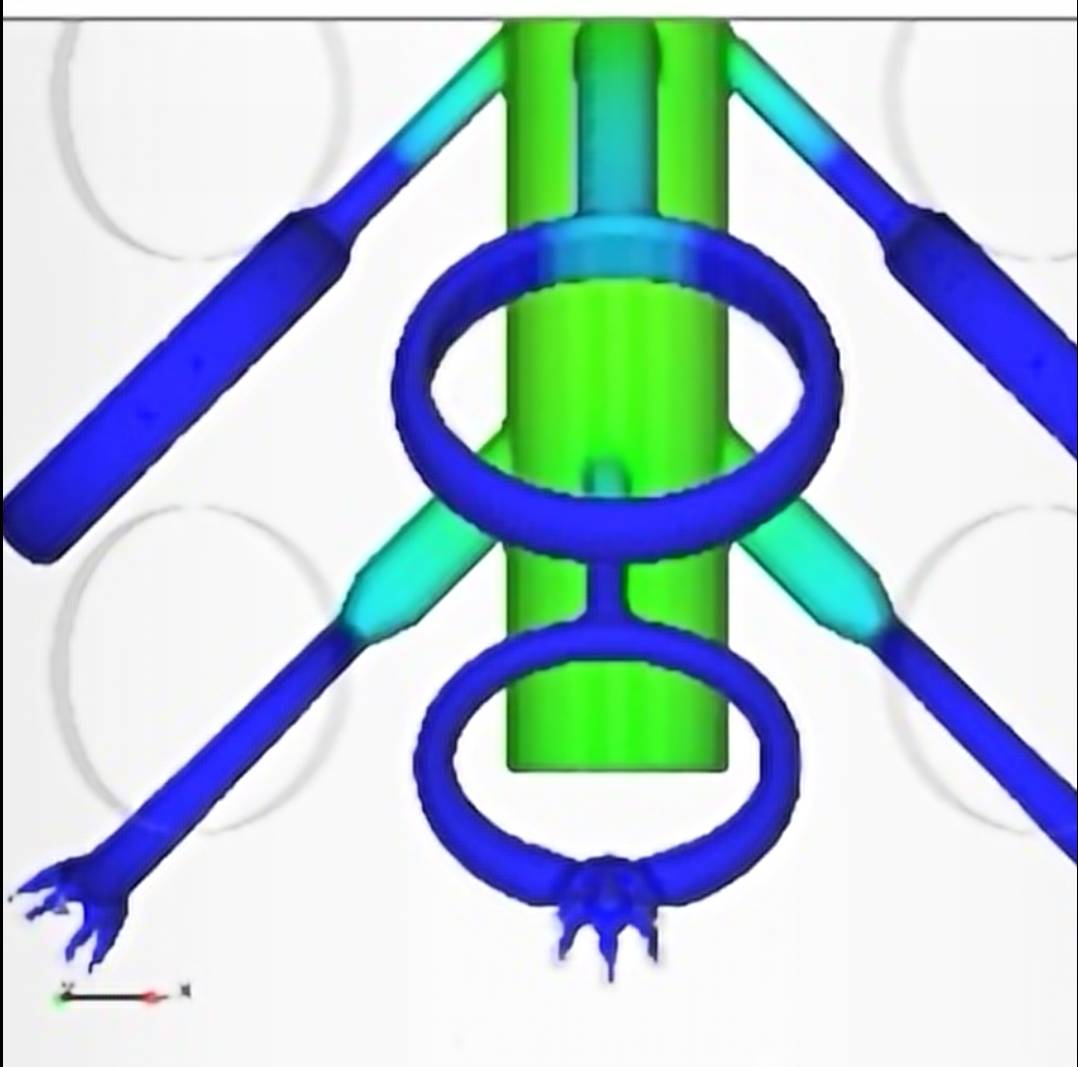
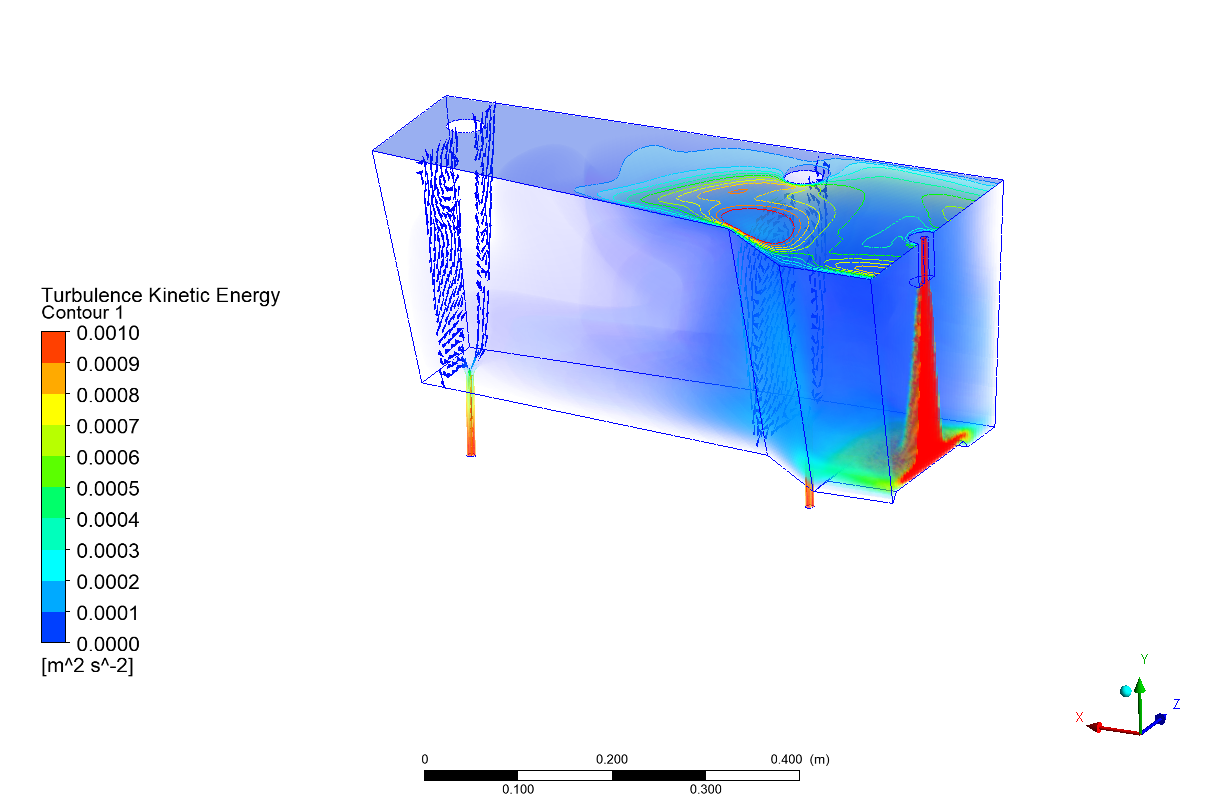
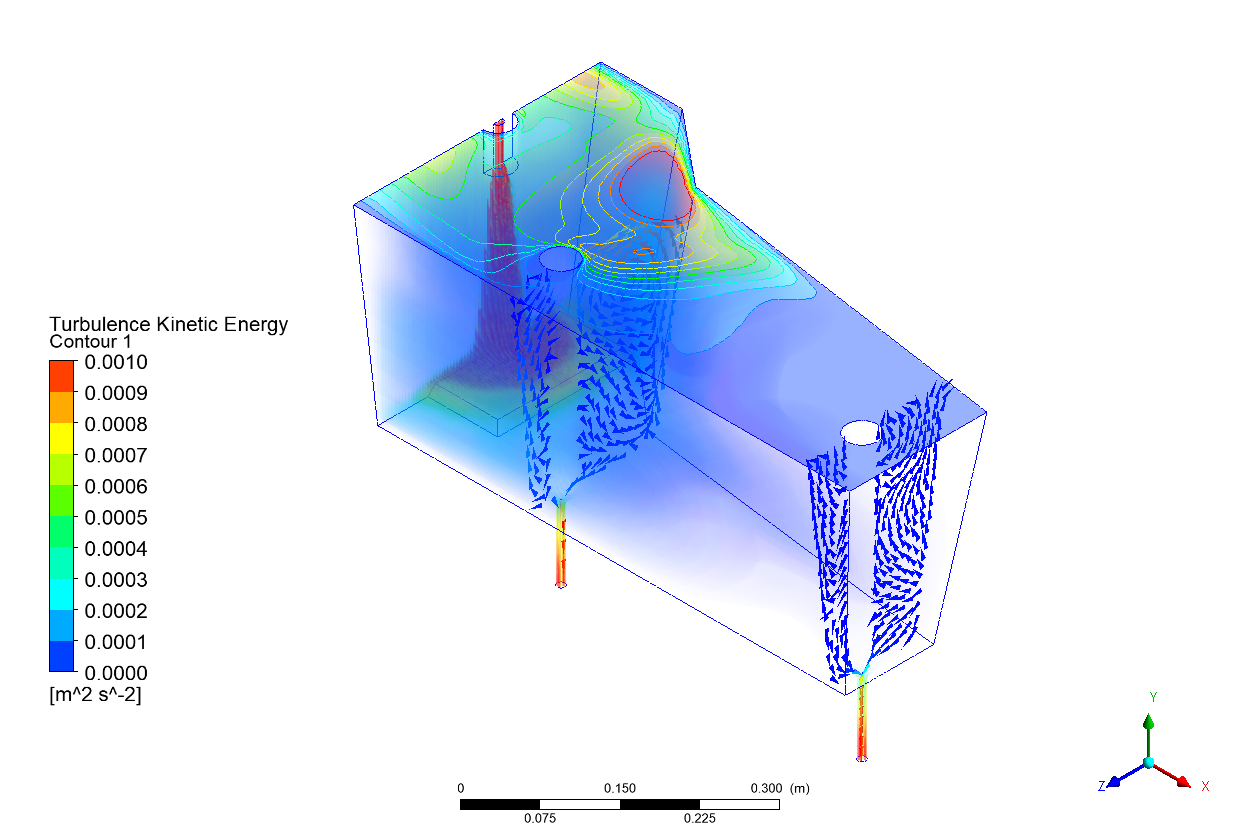
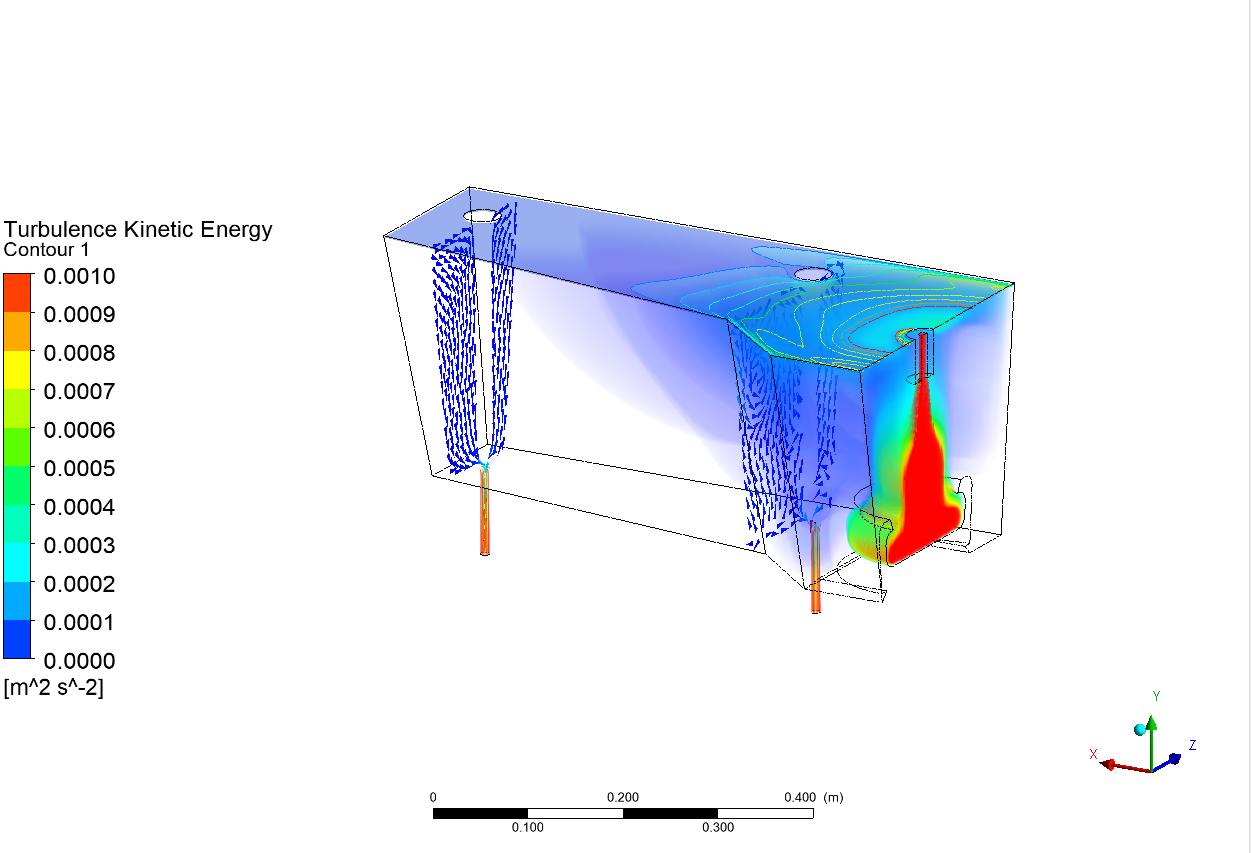
Thesis Title: Numerical Study and Physical Modelling of Flow Characteristics in Tundish by Adjusting Process Parameters
Degree: M.Eng
Publication: Numerical Study of Influence of Casting Speed on Fluid Flow Characteristics in the Four Strand Tundish
Abstract: Steel maker companies attempt to achieve high production quality and decrease production costs due to high competition of the global steel industry. Steel cleanliness plays a significant role in the steel quality which is the key success factor for the steelmaker. In order to optimize the steel cleanliness in the continuous casting process, flow characteristics were studied to enhance the inclusion removal efficiency in four strand tundish. The purpose of this research is to study the effect of casting speed on the flow characteristics of molten steel inside a four-strand tundish. The investigation was carried out by using the commercial computational fluid dynamic (CFD) software ANSYS 18.2. A 1:3 water model tundish based on process parameters from Millcon Steel PLC were employed in this study. The simulation results were validated with the physical water model. The residence time distribution (RTD) curves were applied to analyze the flow characteristics of the tundish. The results of this study show the different casting speeds have an effect on the flow characteristics inside the tundish. The start point of RTD curve of the flow in the tundish with casting speed of 3.0 m/min is the shortest amongst all casting speeds used (1.7, 2.0, 2.3 and 3.0 m/min). A short time period of the start point of RTD curve increases the chance of inclusion contamination in the casting mould and leads to low quality products. Furthermore, the outlet positions affect the minimum residence time of RTD curves and the tracer concentration directly. The RTD start point of the middle outlet located close to the inlet position is faster than that of the far outlet located far from the inlet. The results obtained from the study contributes to the optimization of productivity and quality of the example plant.

2016
Mr. Patiparn Ninpetch

Thesis Title: The study on Metal 3D Printing and Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) process Additive manufacturing
Date of Graduation: 7 June 2019
Degree: M.Eng
Publication:
1. P. Ninpetch, P. Kowitwarangkul, S. Mahathanabodee, R. Tongsri, & P. Ratanadecho, Thermal and Melting Track Simulations of Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF), IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 526, (2019): 1-4, DOI: 10.1088/1757-899x/526/1/012030
Abstract: Laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) process involves with the construction of phase transformation, melting, and rapid solidification of weld metal powder bed which affects the properties and the microstructure of final parts, e.g. density, dimension, mechanical properties, void, porosity, and non-fully melted particle. The aims of this work were to study the effect of process parameters, e.g. laser power and scanning speed, on the temperature field and melt pool geometry and the characteristics of single melting track in the L-PBF process by using the commercial
CFD software simulation Flow-3D (Flow-weld). The laser power, scanning speed, laser spot diameter, and layer thickness varied in this study were 120 W, 140 W, 0.4 m/s, 0.6 m/s, 0.8 m/s, 80 µm and 50 µm respectively. The results stated that at the lower scanning speed, the temperature field has a region of heat distribution larger
than that of the higher one. The geometry of melt pools can be changed from ellipse shape to tear drop shape when the scanning speed is increased. The width and depth of laser melting track is increased when the higher laser power and lower scanning speed are applied. The void is found underneath the laser melting track when the scanning speed changes from 0.4 m/s to 0.6 m/s.
2. P. Ninpetch, P. Kowitwarangkul, A Numerical Study on the Thermal Transient Model with Moving Laser Heat Source of AISI 304 Stainless Steel Plate, Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol. 17, (2019): 1761–1767. DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.208
Abstract: Laser beam is commonly used as a moving heat source in various metal processing such as cutting, heat treatment, welding, and recently in additive manufacturing or metal 3D-printing. Understanding of thermal behavior resulting from a moving laser beam are essential to control the product quality in those processes. This research aims to study the 3D thermal transient model of moving laser heat source with changeable direction of motion in order to investigate the effect of process parameters, e. g. , power intensity, scanning speed and hatch spacing on the temperature distribution of the AISI 304 stainless steel plate. The numerical study is carried out using the commercial software ANSYS 18.1 and considering the simulation of the low intensity laser heat flux with Gaussian intensity distribution. The results of temperature profile at the probe point from numerical simulation are in agreement with the experiment results.
3. P. Ninpetch, N. Teenok, P. Kowitwarangkul, S. Mahathanabodee, R. Tongsri and P. Ratanadecho, The Influence of Laser Parameters on the Microstructure and the Micro Hardness of AISI 316L Fabricated by L-PBF process, Proceedings of The 8th Asia Pacific IIW international conference congress, Bangkok, Thailand, 20th – 22th March 2019, IIWAP2019-A03, pp. 39-44.
Abstract: Laser powder bed fusion process (L-PBF) is the most widespread additive manufacturing (AM) process which uses laser source scanning as a moving heat source on powder bed to fully melt the metal powder in a layer-bylayer fashion. During the process, it involves various complex multiphysics such as materials absorption, heat transfer, molten fluid flow, phase transformation etc. These physical phenomena have significant effect on physical properties, mechanical properties and the microstructure of final parts. The present study aims to investigate the influence of laser parameters including scanning speed and hatch spacing (distance between laser scanning track) on the laser melted track width, layer formation, microstructure and microhardness of AISI 316L stainless steel fabricated by Laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) process with low laser power (Max. 50W). The experimental results presented that the laser melted track width is decreased from 250 to 150 micron when the scanning speed is increased from 5 to 15 mm/s. The discontinuous melted track with balling effect can be observed in the layer formation at the scanning speed of 5 mm/s. When the scanning speed is increased to 10 mm/s, more continuous laser melted track was formed. The microstructure of AISI 316L stainless steel fabricated by L-PBF process consists of cellular columnar structure and dendrite structure oriented according to temperature gradient direction during rapid cooling.

Mr. Sathaporn Lakkum

Thesis Title: Numerical and Physical Modeling of the Mixing Process in Gas Stirred Ladle System
Degree: M.Eng
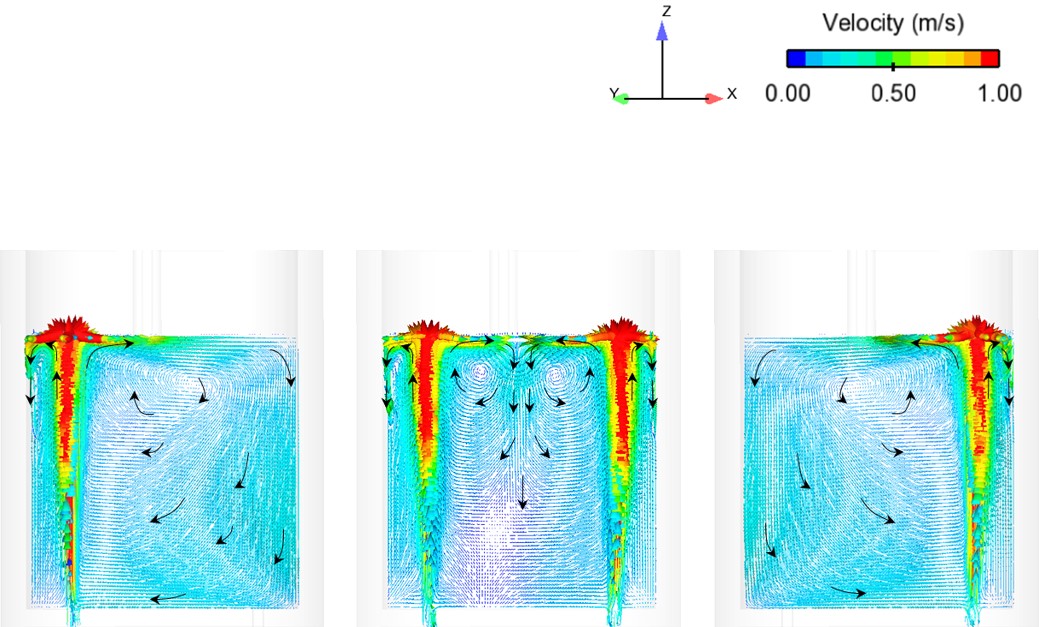
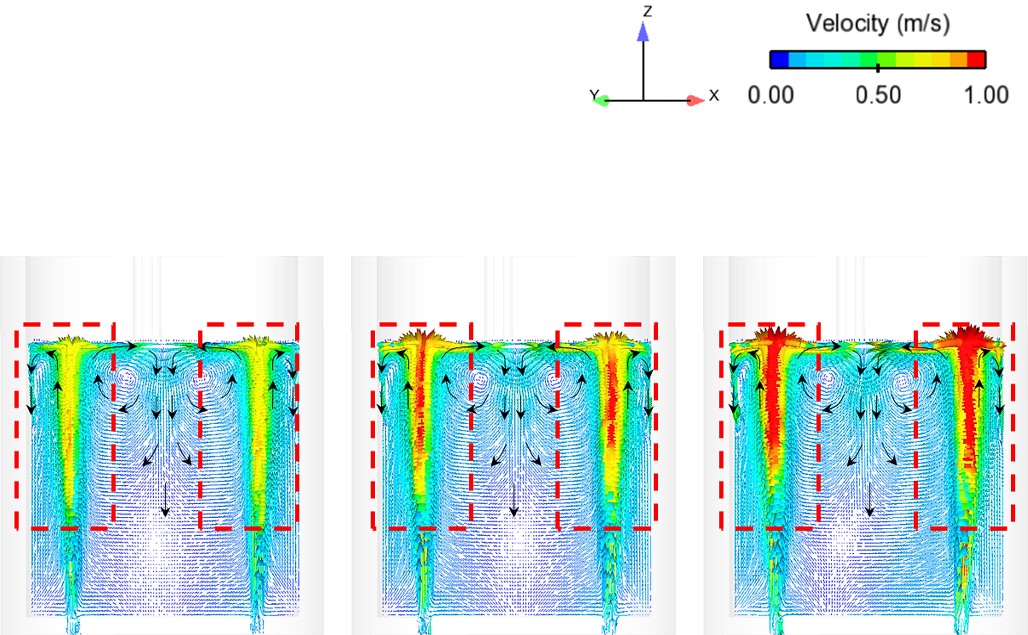
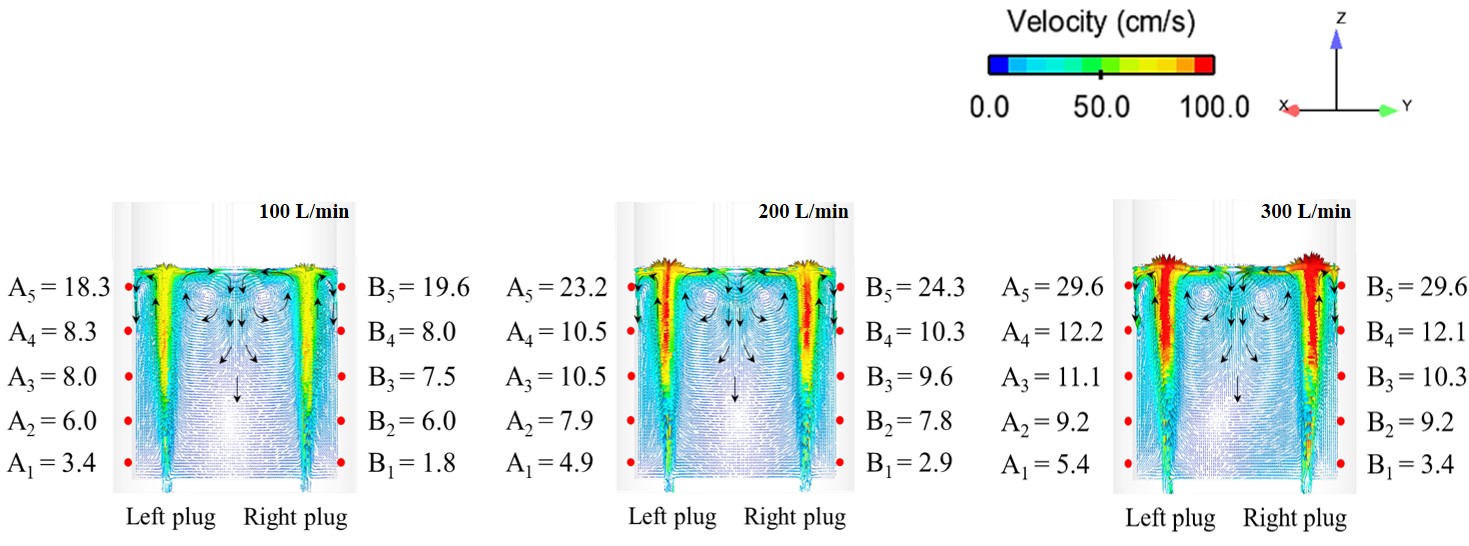
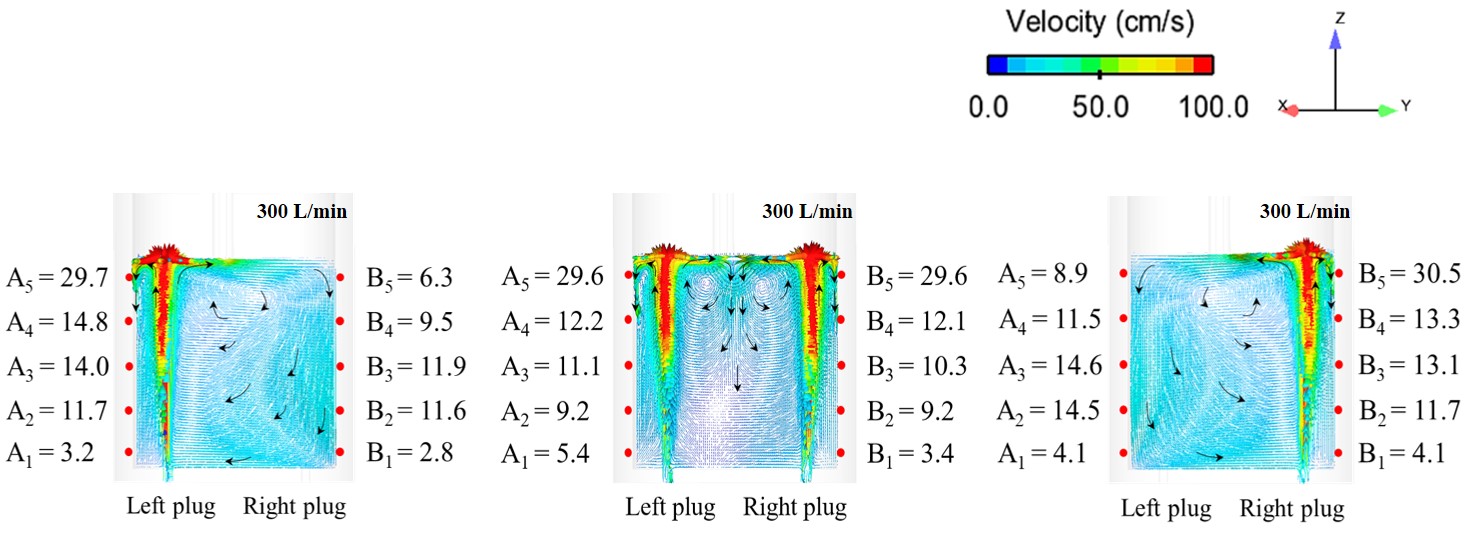
Publication: S. Lakkum, P. Kowitwarangkul, Numerical Investigations on the Effect of Gas Flow Rate in the Gas Stirred Ladle with Dual Plugs, Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 526, (2019): 1-4, DOI: 10.1088/1757-899X/526/1/012028
(Published in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 526, 2019, pp. 1-4)
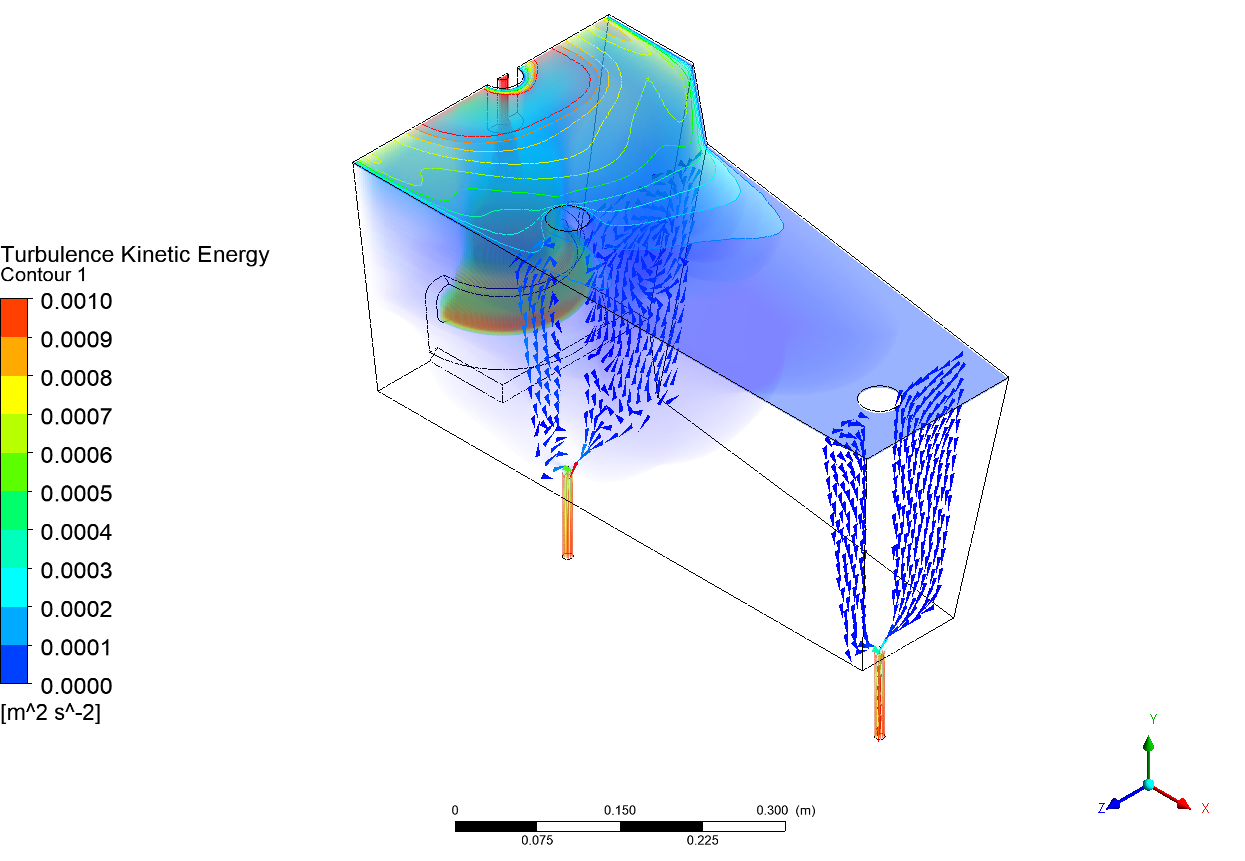
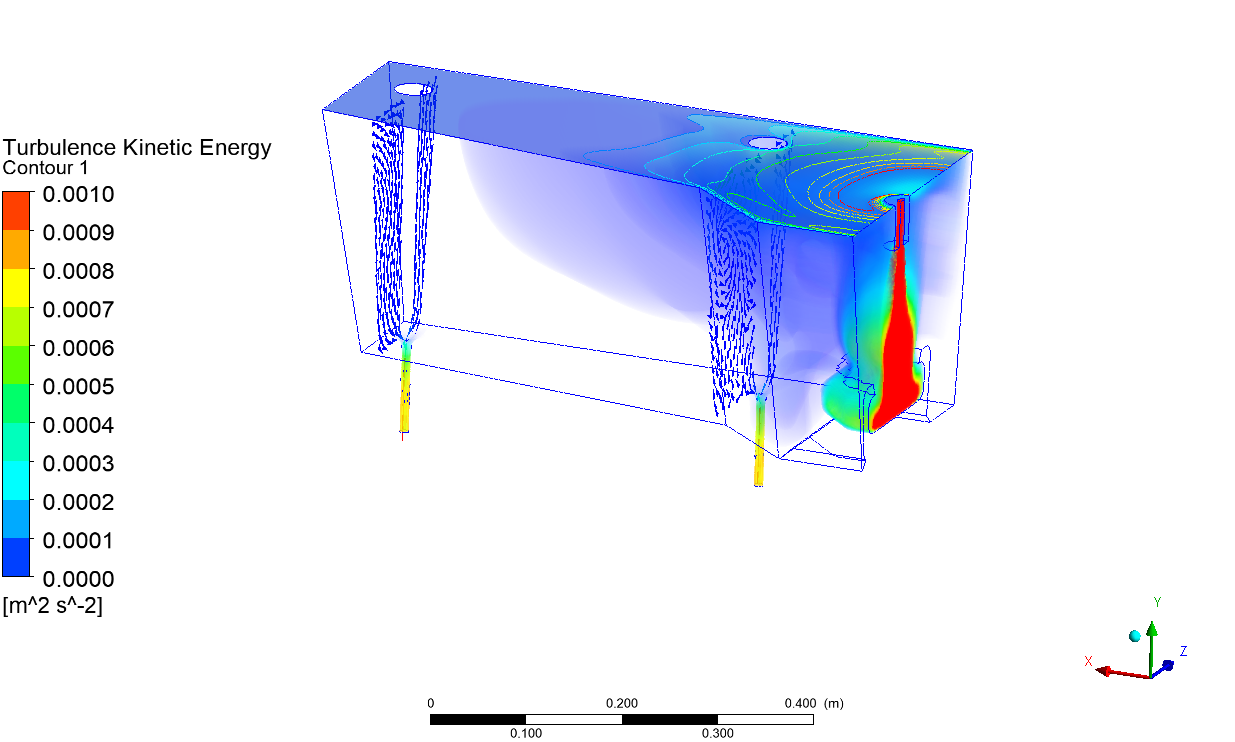
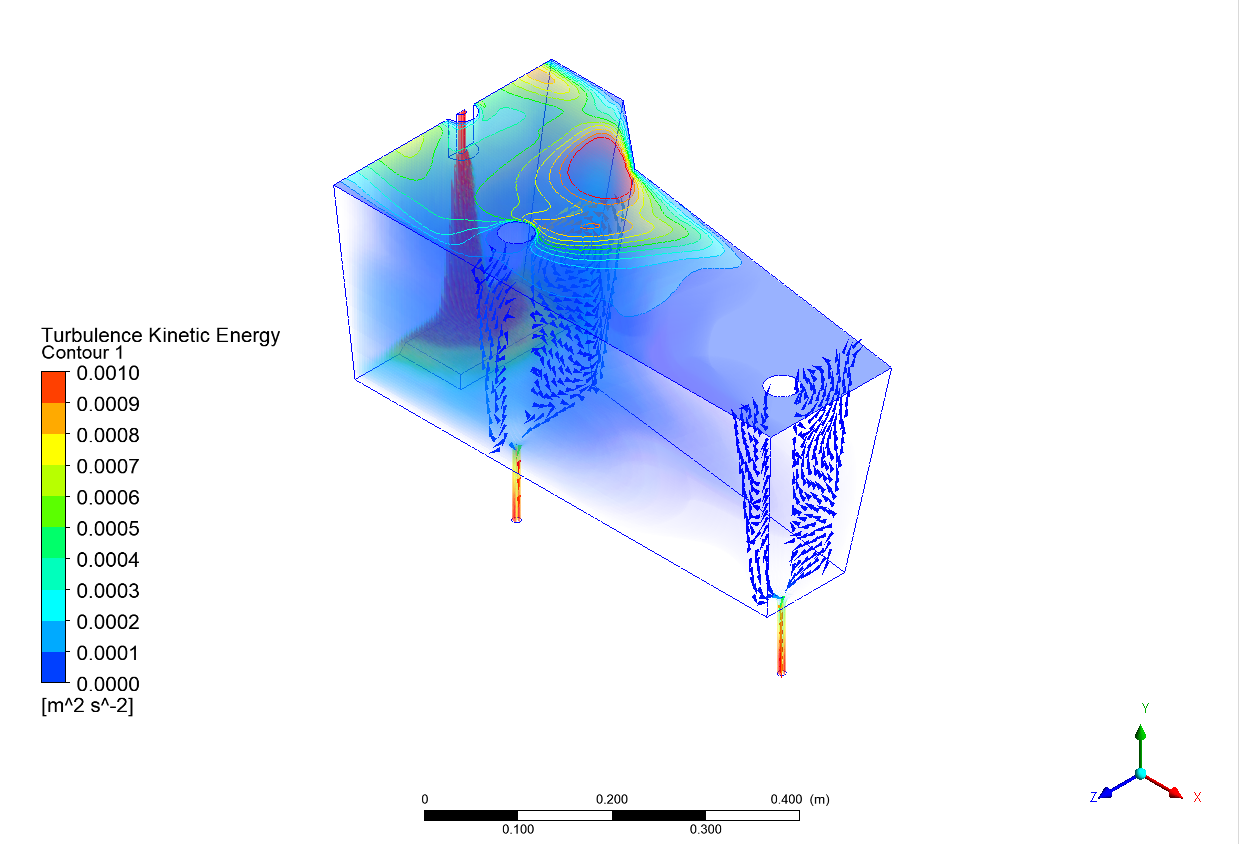
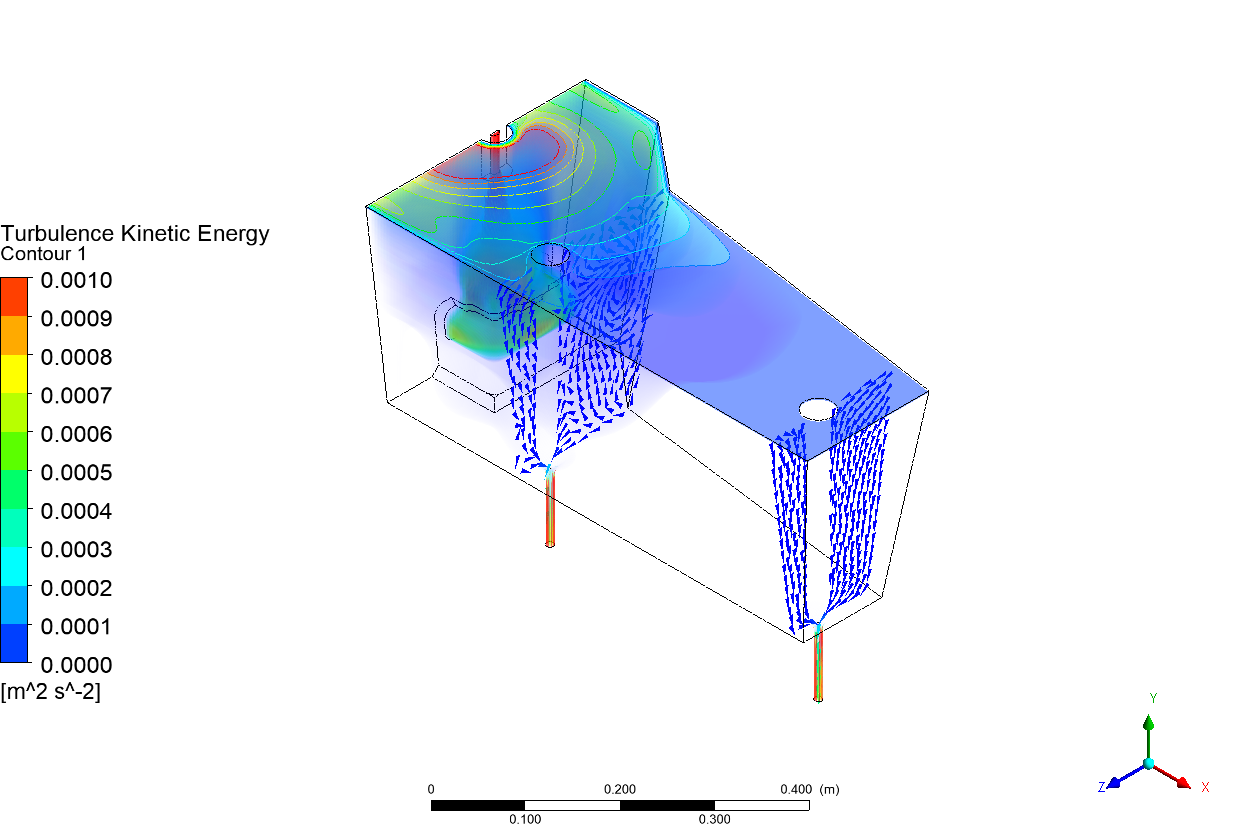
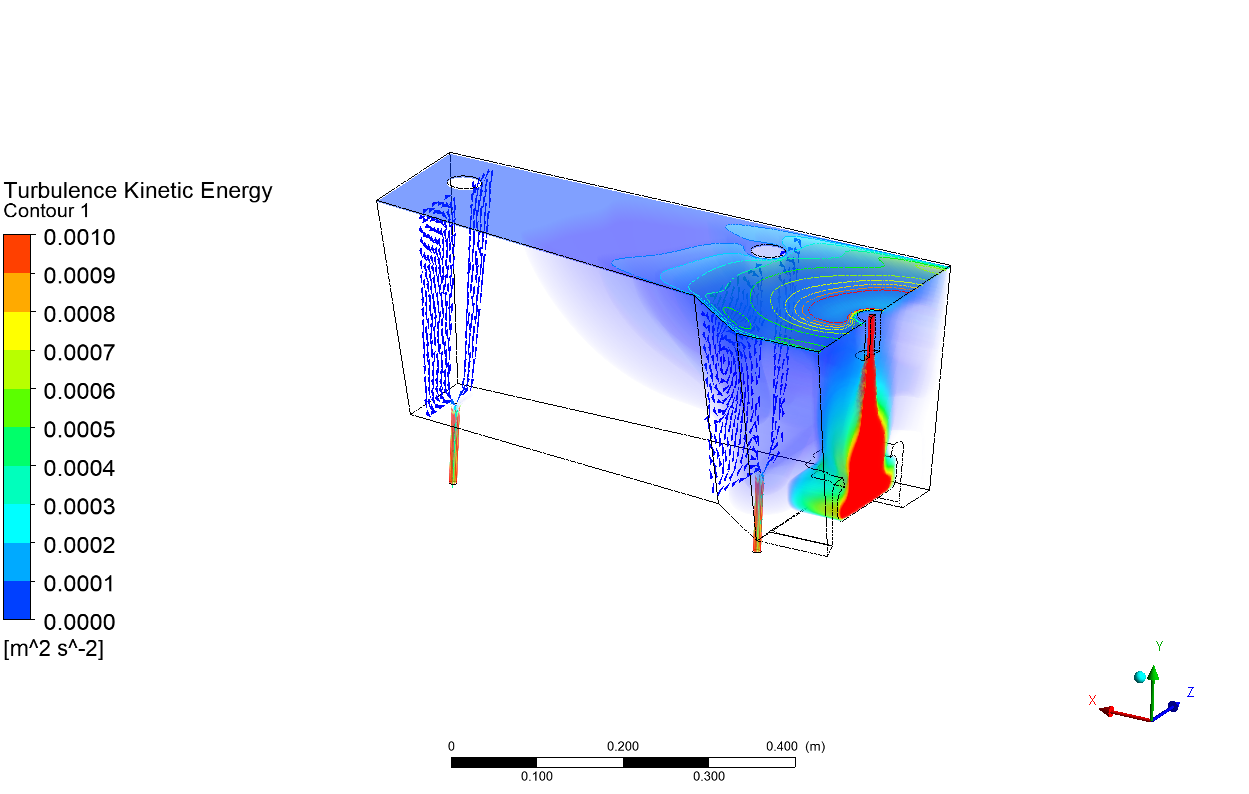
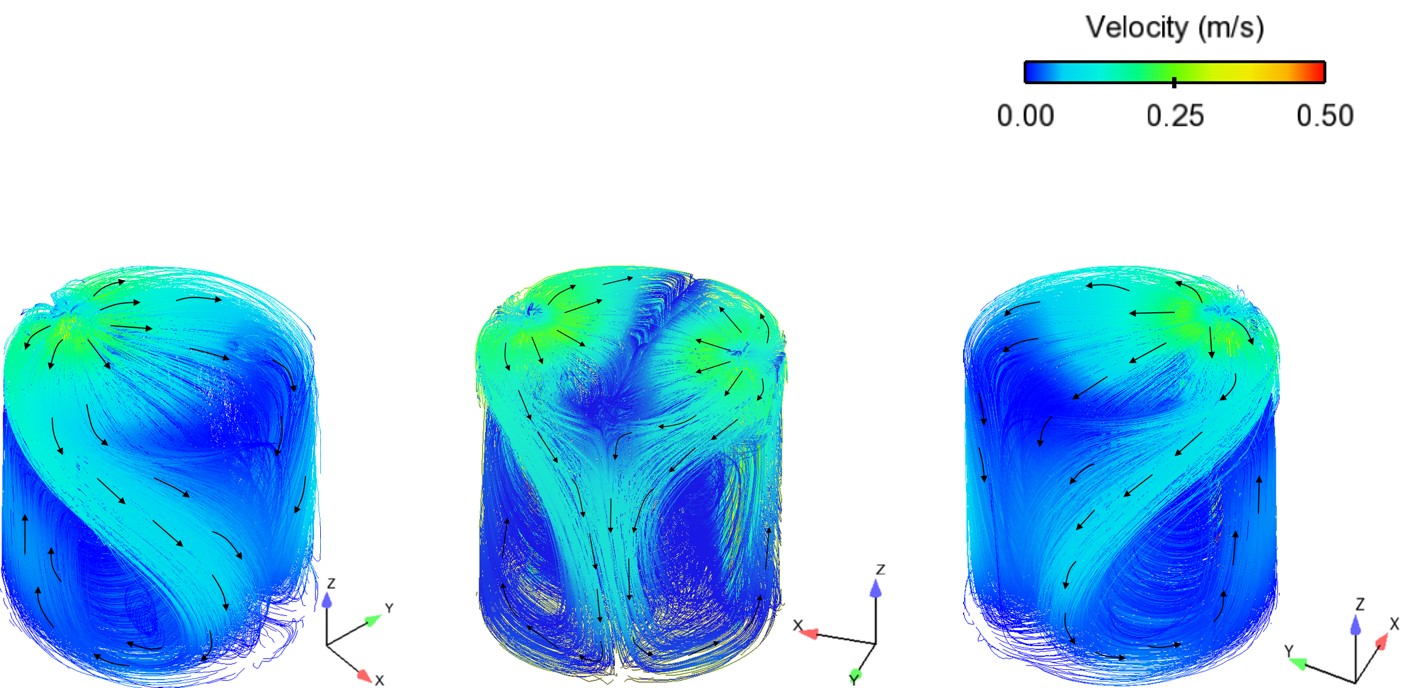
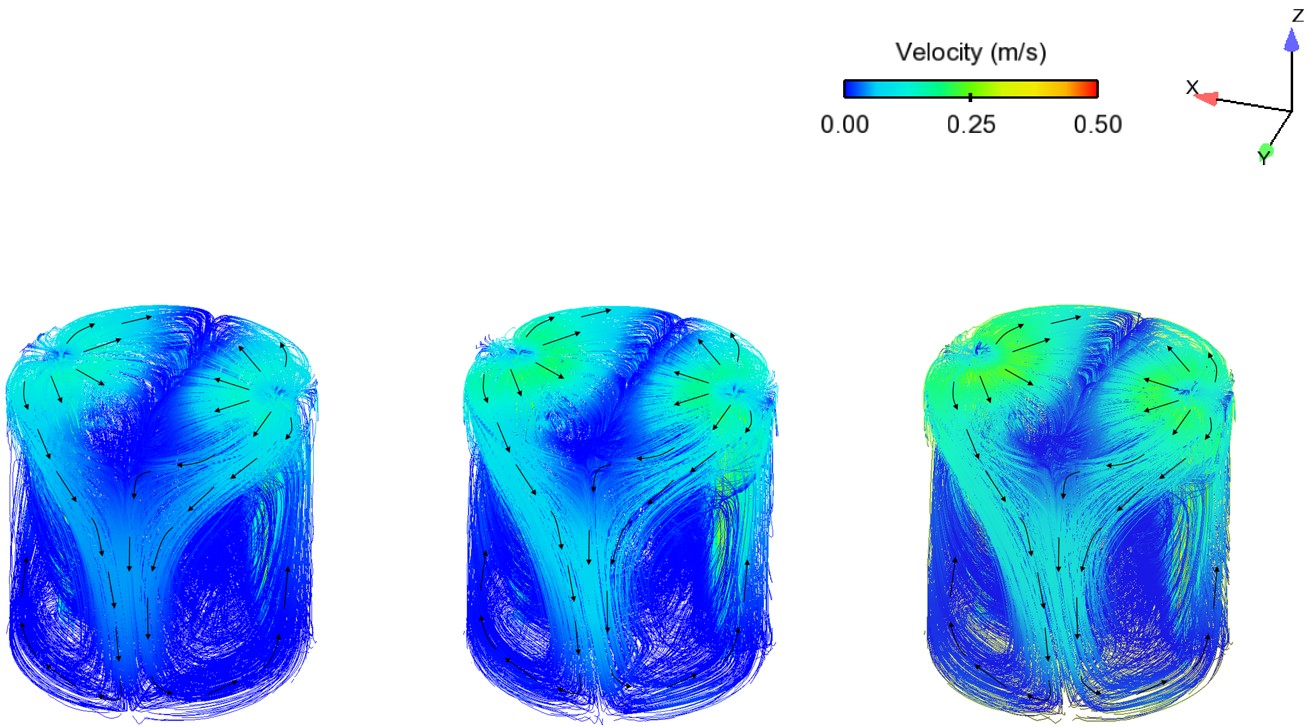
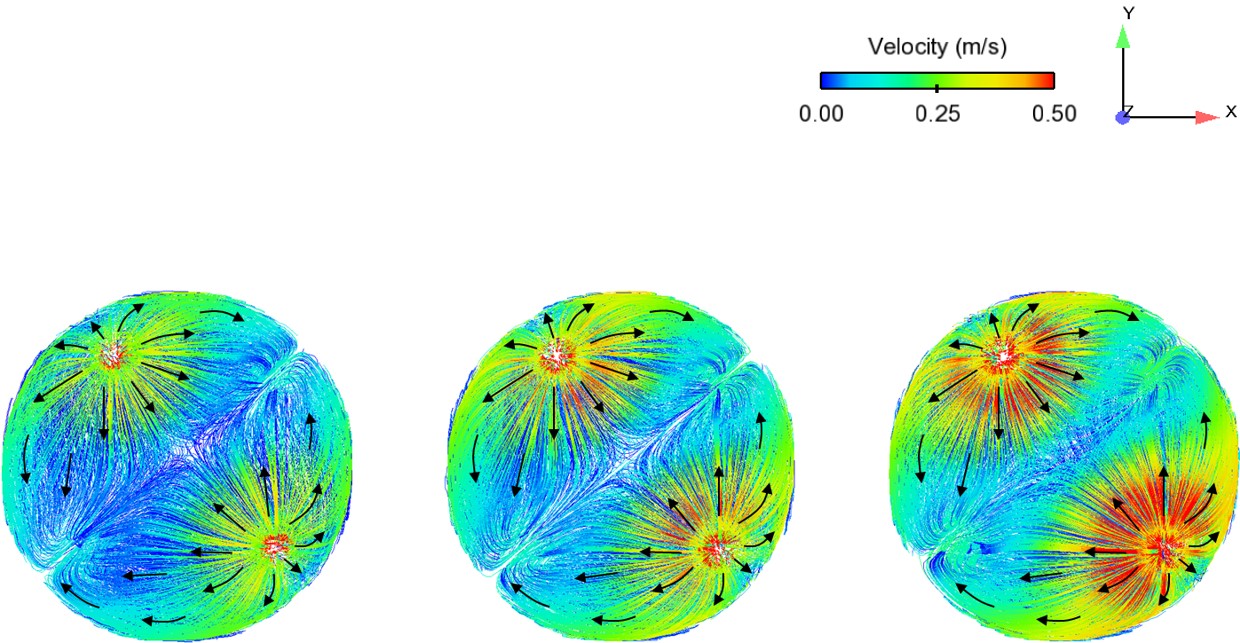
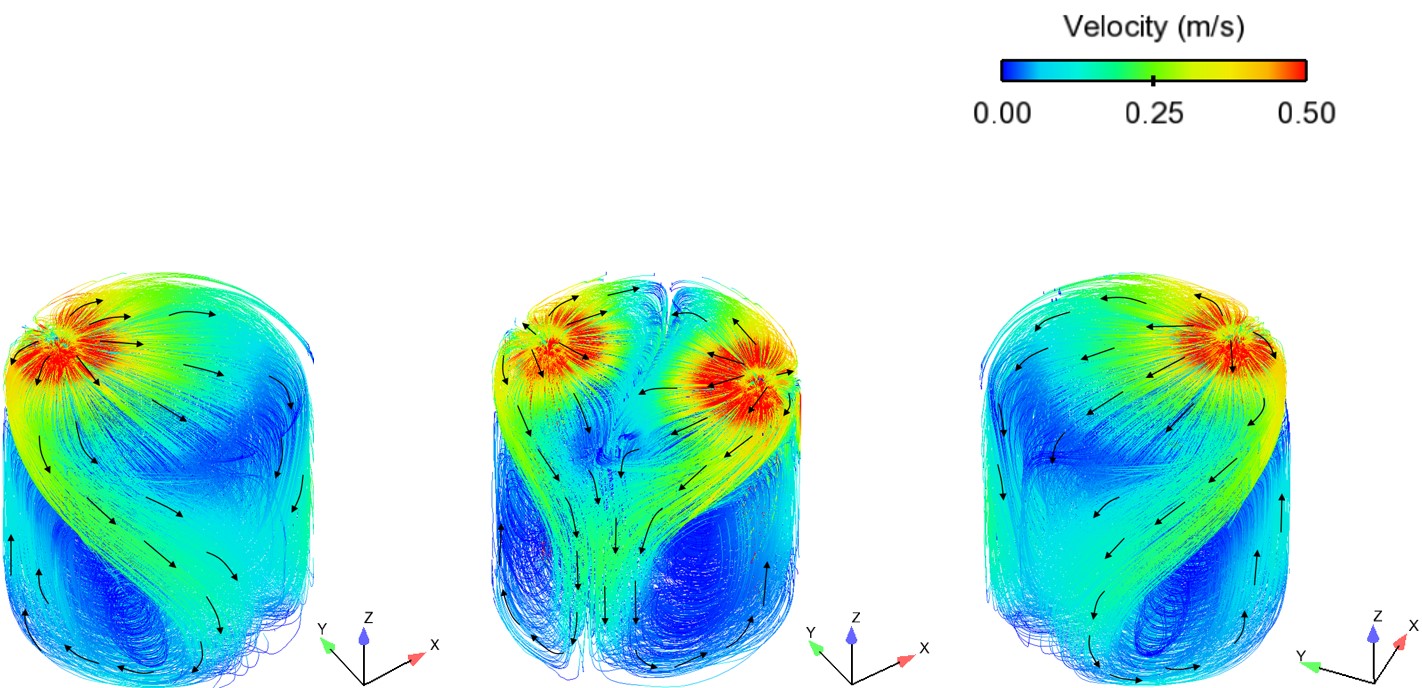
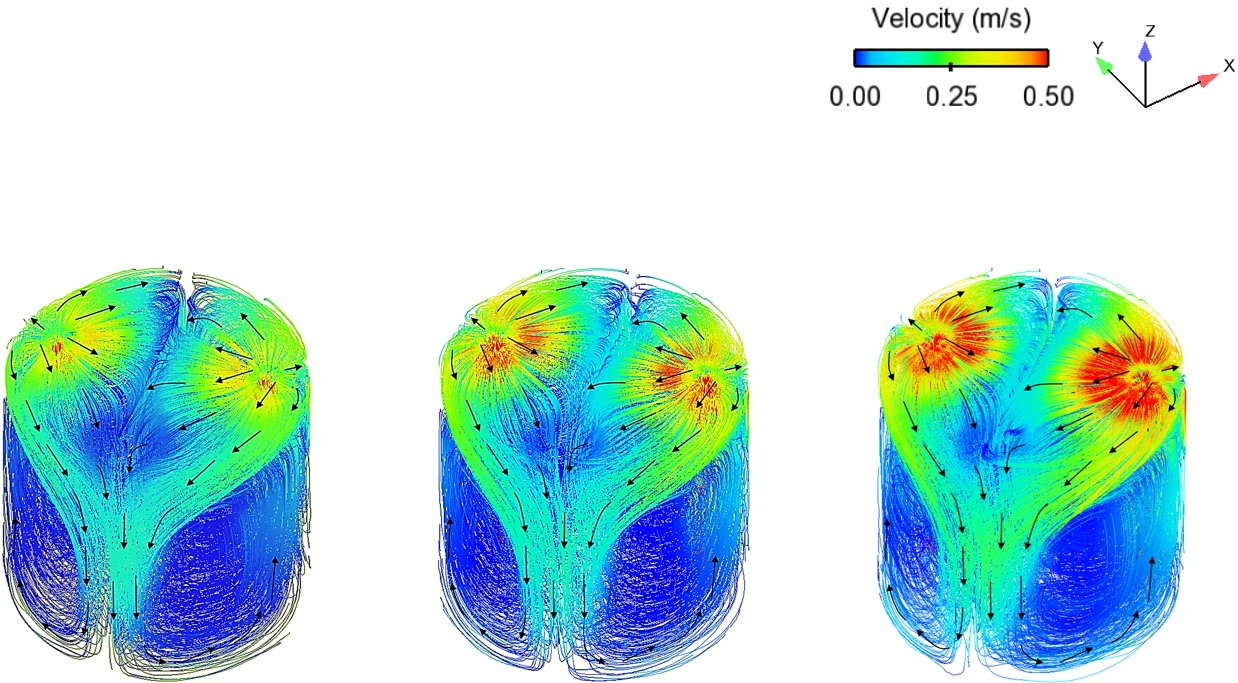
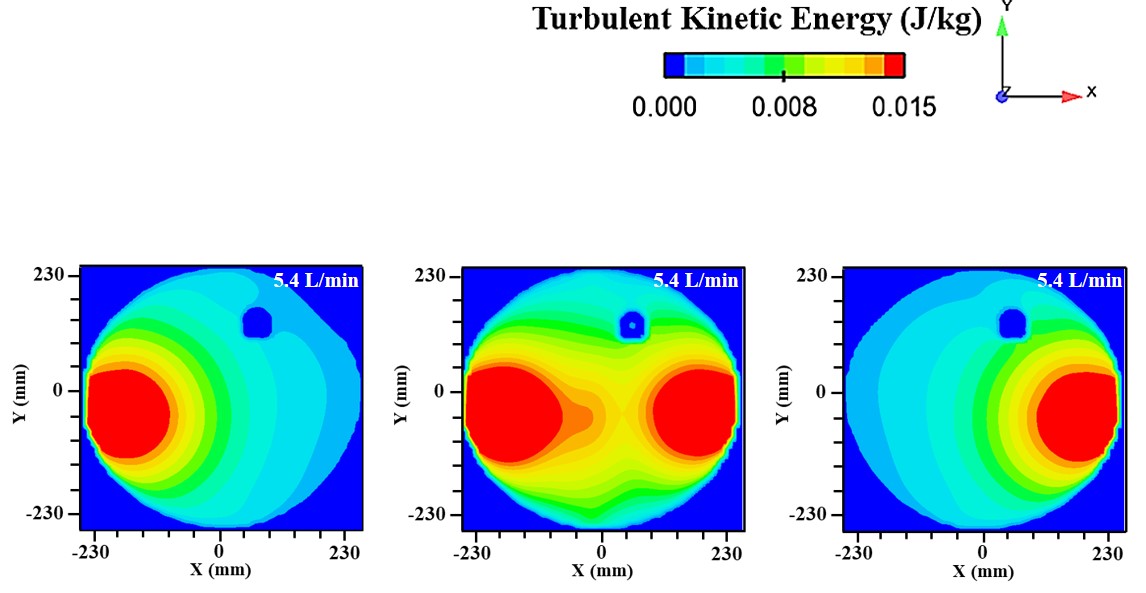
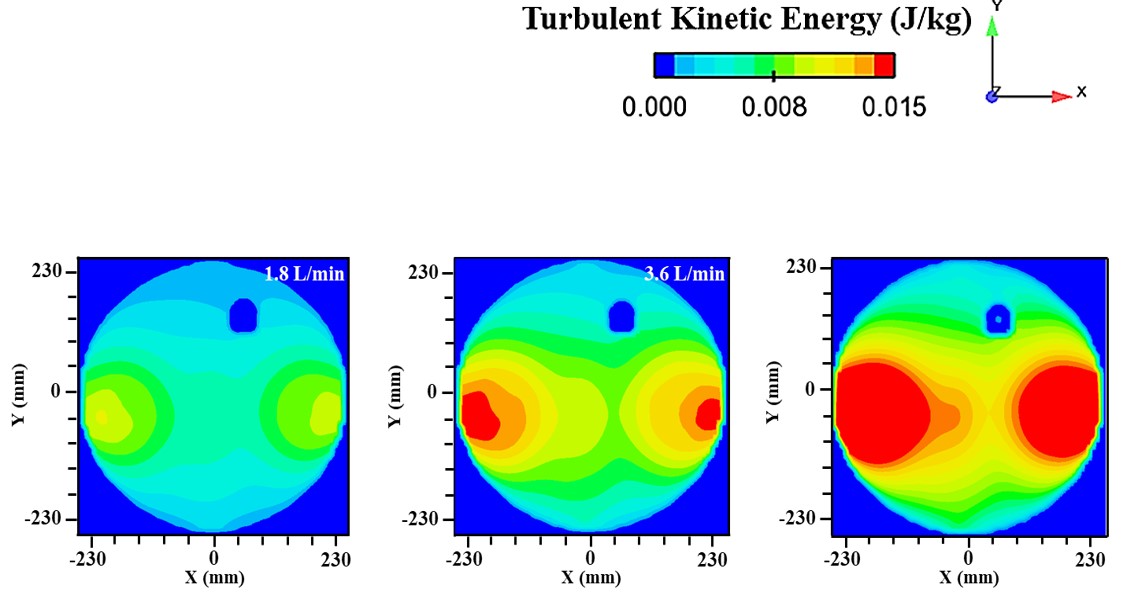
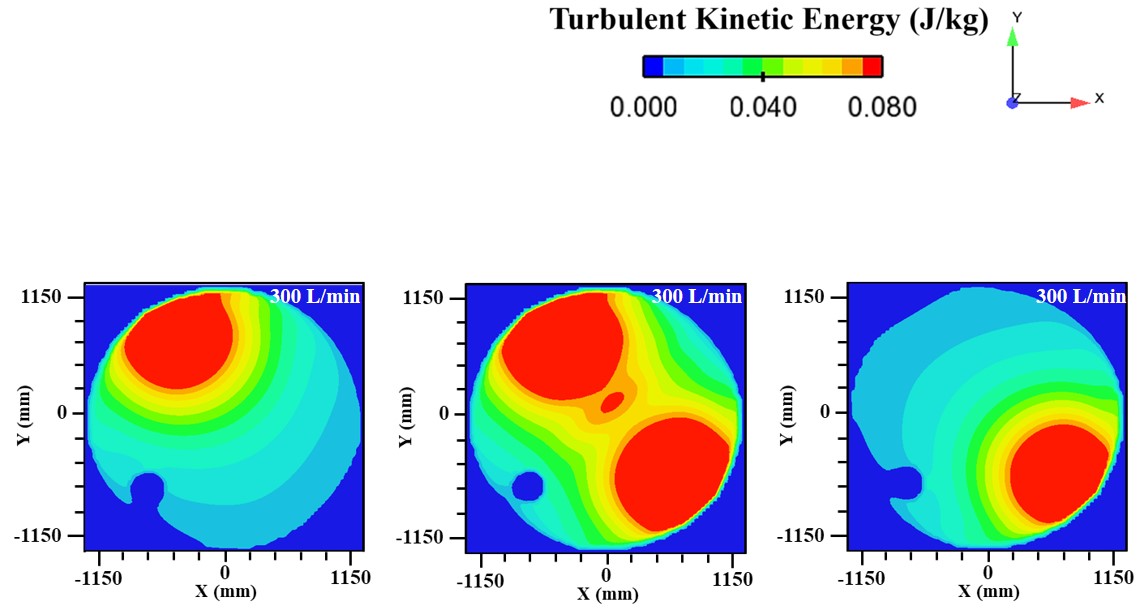
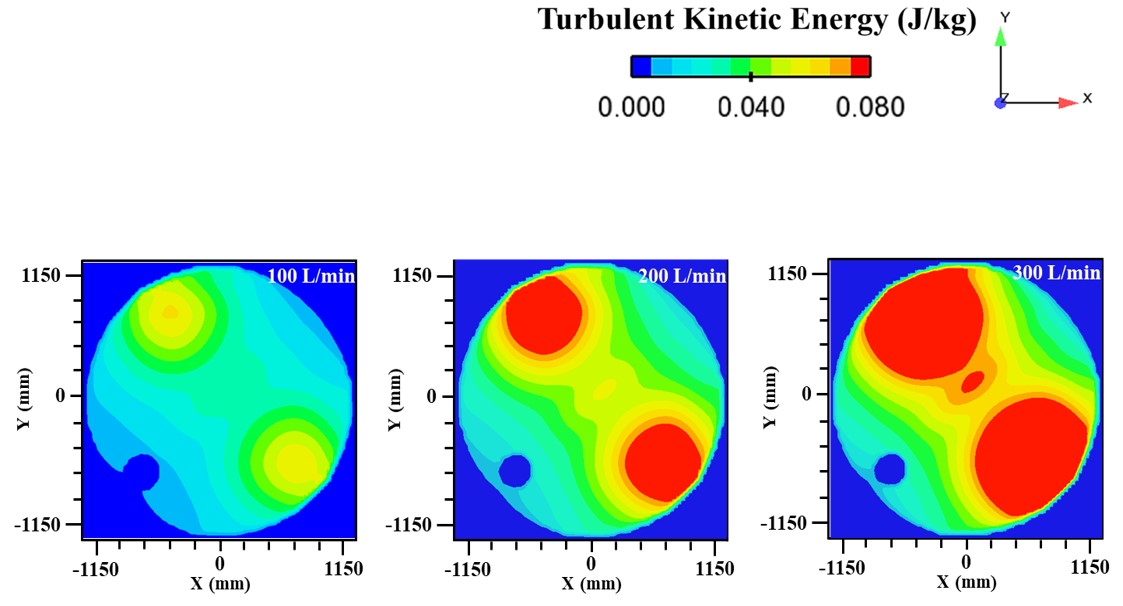
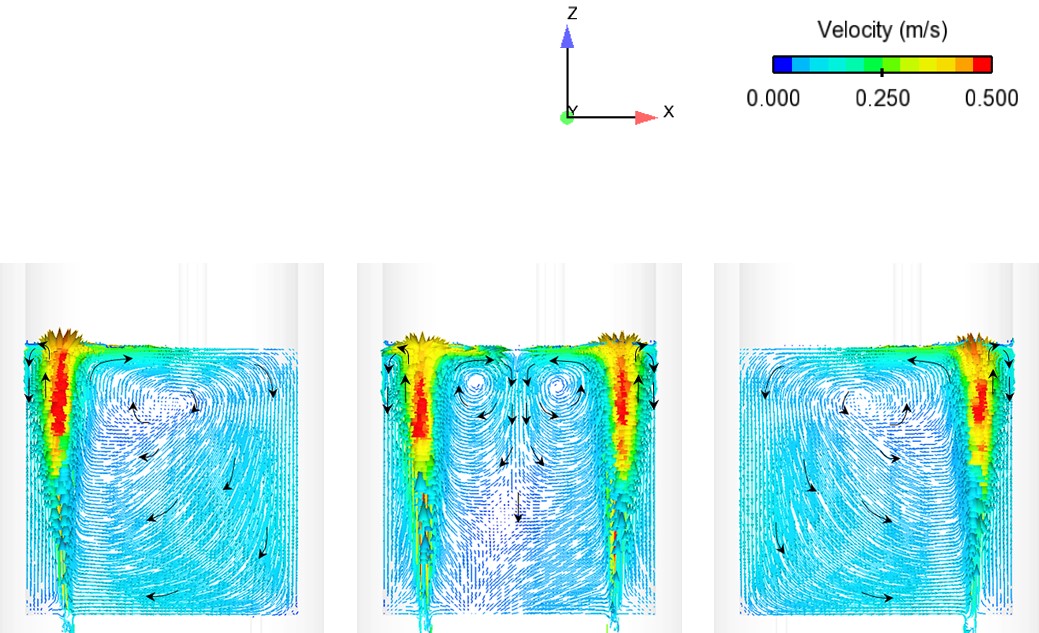
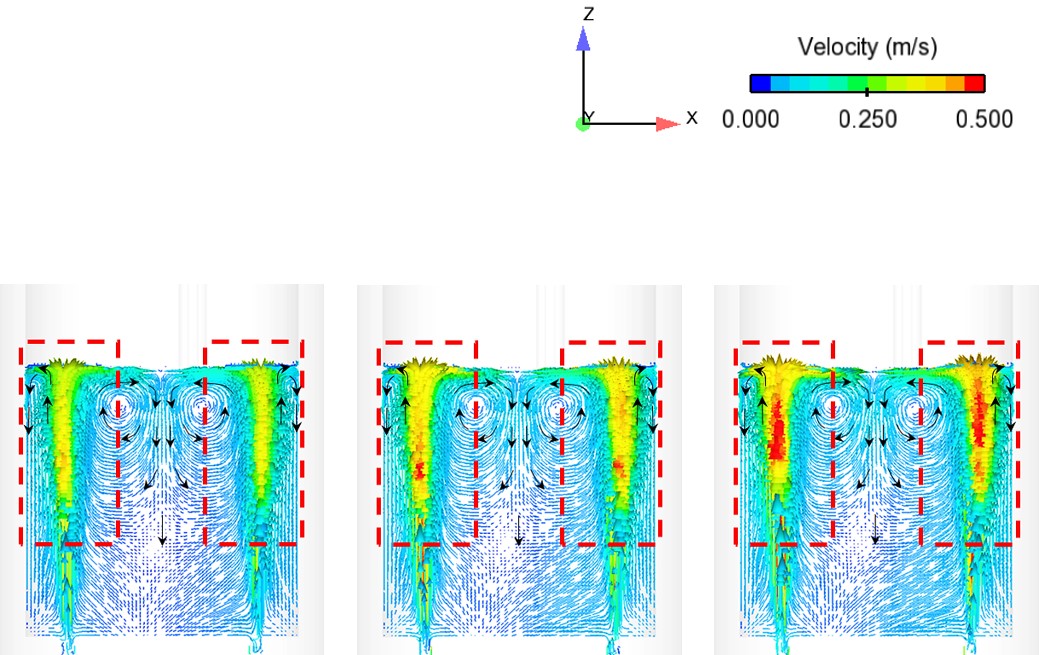
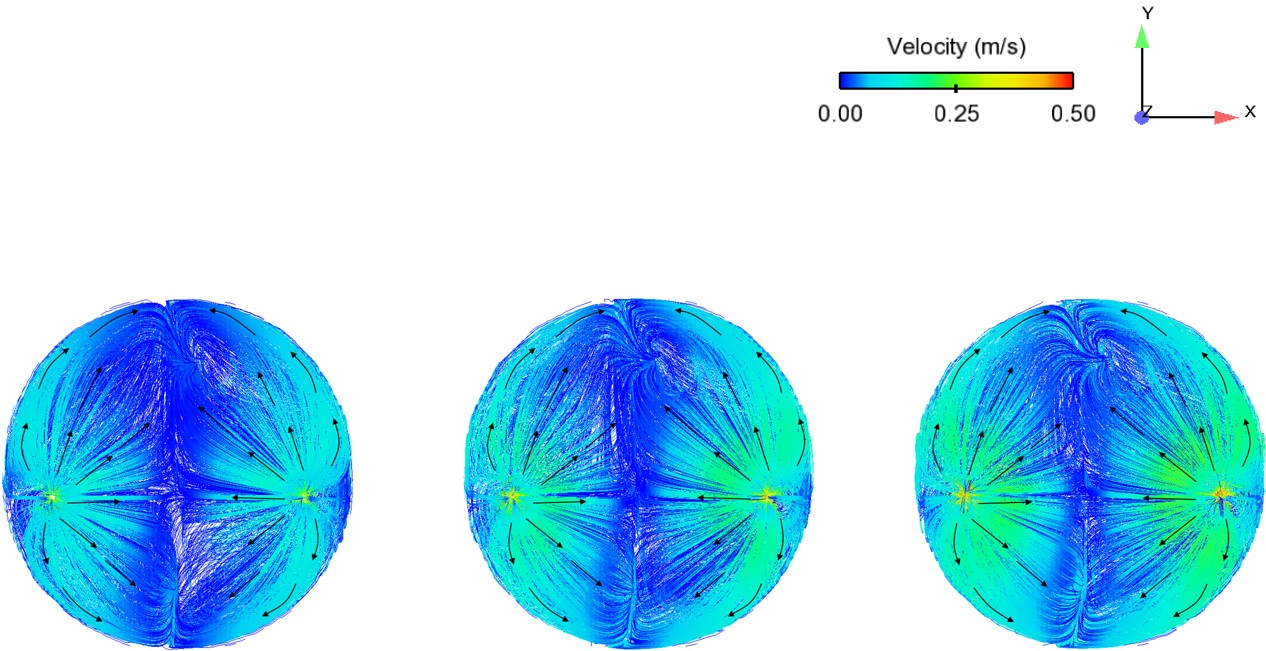
Abstract: Ladle or secondary steelmaking is an essential metallurgy process in which the steel is adjusted to the chemical compositions required in the final product. The objective of this study was to predict 95% mixing time curve using CFD simulation in order to investigate the possibility to optimize the gas flow rate in gas stirred ladle systems. The commercial software, Flow-3D, was used in this study. This study was divided into three parts. The first two parts of the study was the investigation of the effects of bubble sizes and diffusion coefficient on the mixing time by setting constant-volume gas flow rate. The last part was the study of the effect of gas flow rate on the mixing time. The ladle geometry and operation condition from the example steel plant, Millcon Steel PLC were used in this study. The simulation results indicated that different sizes of bubble have minor effects on the mixing time. The investigation of the effect on the mixing time with and without diffusion coefficient showed that the diffusion coefficient has no significant influence on the mixing time but has significant effects on the characteristics of the plume regions and the velocity flow field. Finally, it was found that gas flow rate has significant effects on turbulent kinetic energy, the mixing time and the steel cleanliness. The results can support the example steel plant to optimize the mixing process concerning productivity and cleanliness quality of the liquid steel.

Mr. Adisorn Piyapaneekoon

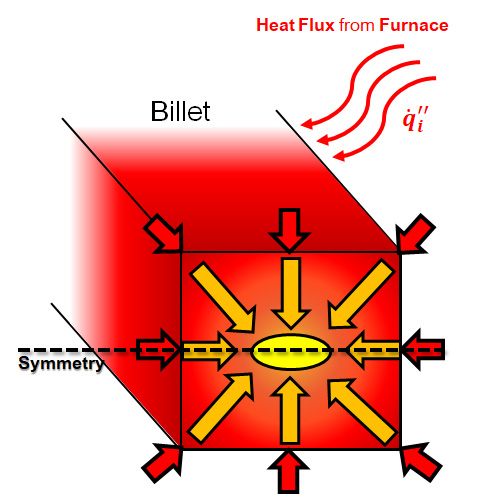
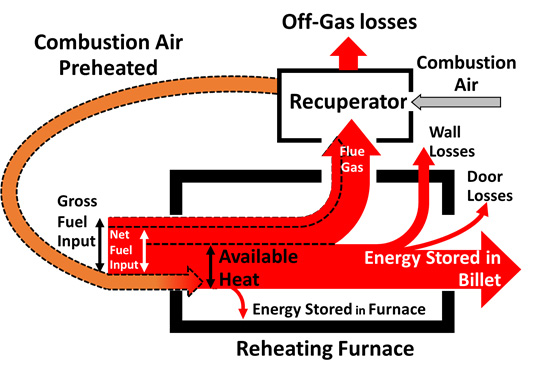
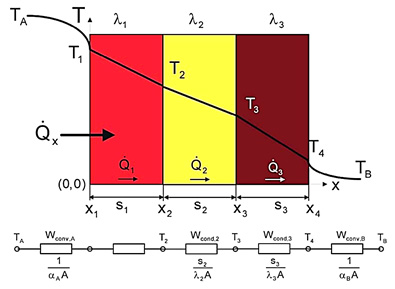
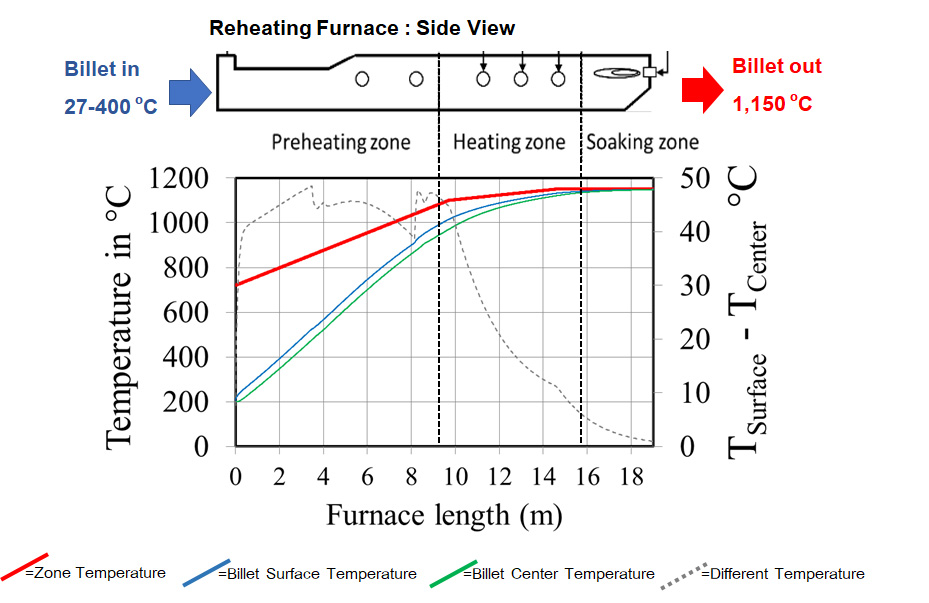
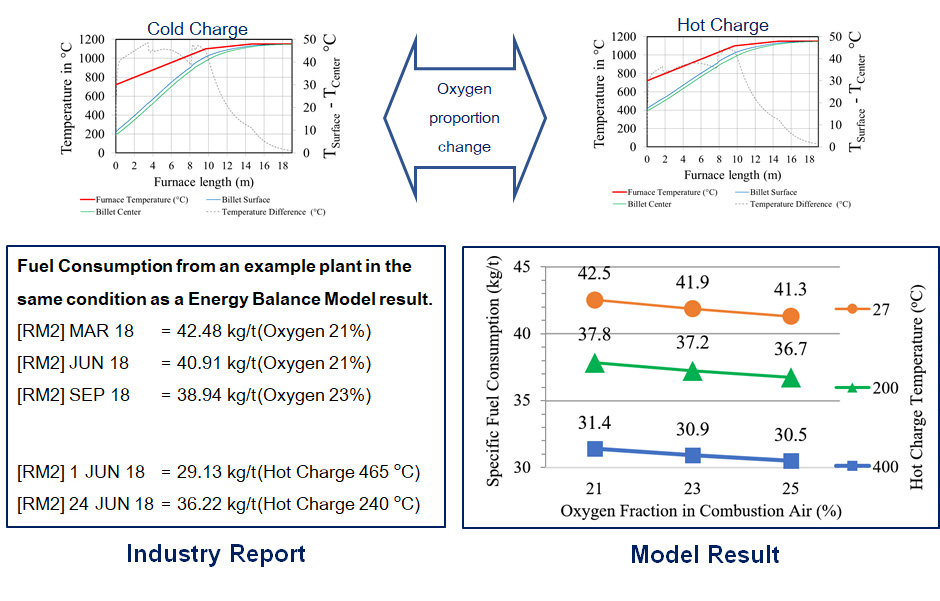
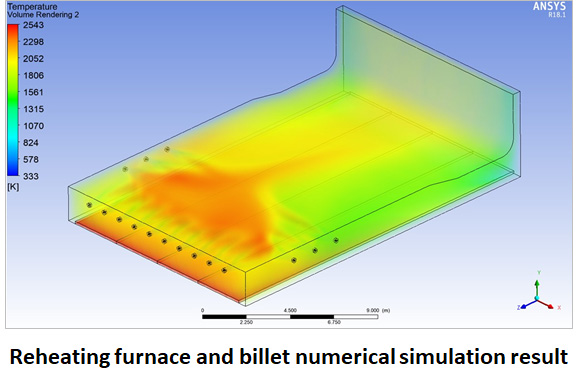
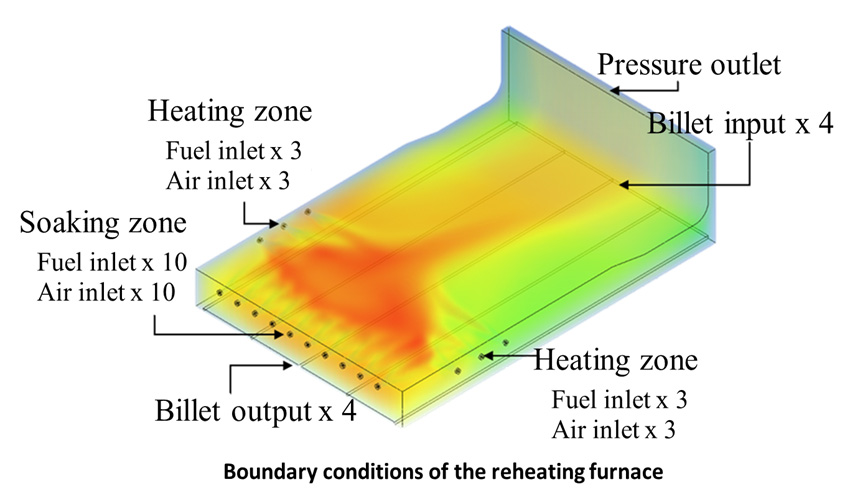
Thesis Title: Modelling of the Reheating Furnace and Energy Efficiency Improvement
Degree: M.Eng
Publication: A. Piyapaneekoon, P. Kowitwarangkul, The Study of Energy Efficiency and Development of Energy Balance Model in the Reheating Furnace, Proceeding of The 8th Asia-Pacific IIW International Congress, 2019, pp. 171-175.
(Published in Proceeding of The 8th Asia-Pacific IIW International Congress, 2019, pp. 171-175)
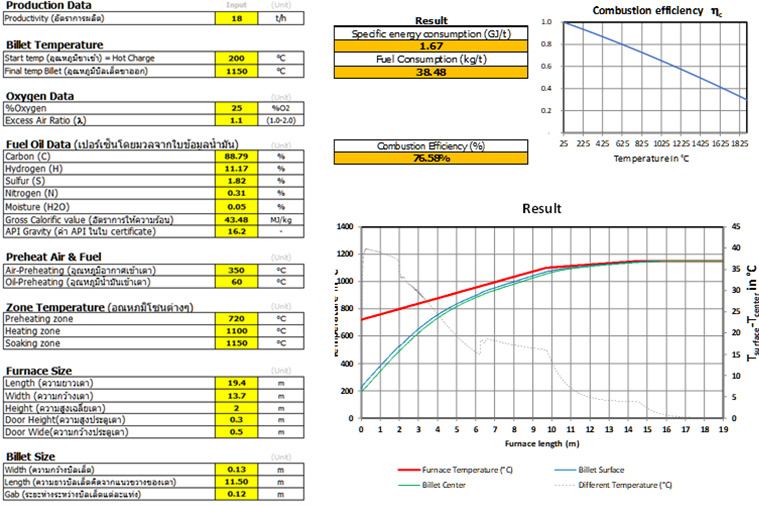
Abstract: One of the high energy consumption industries in Thailand is the hot rolling steel plant. In the rolling mill, a specific energy consumption in reheating furnace plays the most important role in reduction of total energy cost which is the main operation cost in hot rolling steel production. Several hot rolling steel plants in Thailand use fuel oil as a reheating furnace energy source. The purpose of this study is to develop a model that can calculate the specific energy consumption in hot rolling process using fuel oil as an energy source and to study effects of parameters in reheating furnace. The furnace and fuel data from the example steel company, Bangkok Steel Industry PCL were used in this study. The energy balance model of reheating furnace was developed and billet temperature profile can be derived from this model. The investigation shows that, the oxygen enrichment is able to reduce the specific fuel consumption in the example plant. The hot charge temperature is able to reduce the specific fuel consumption significantly depend on temperature of billet and the effect is increased at the high hot charge temperature.

2015
Mr. Perawat Thongjitr

Degree: M.Eng
Date of Graduation: 21 December 2018
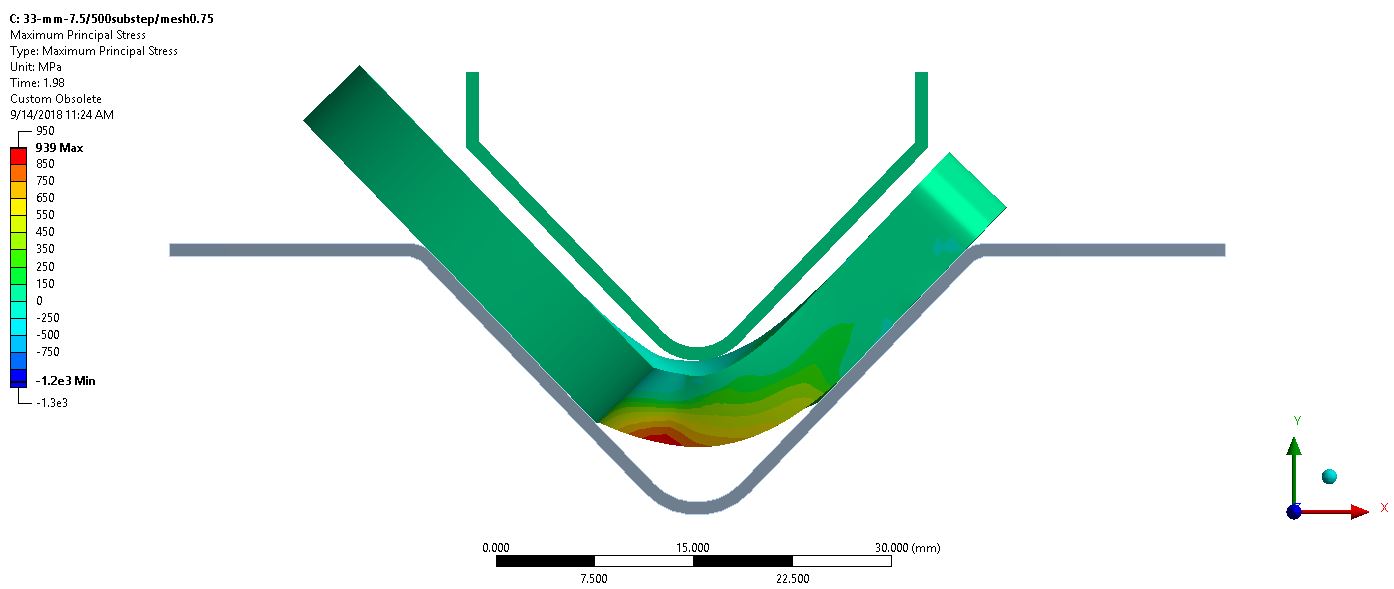
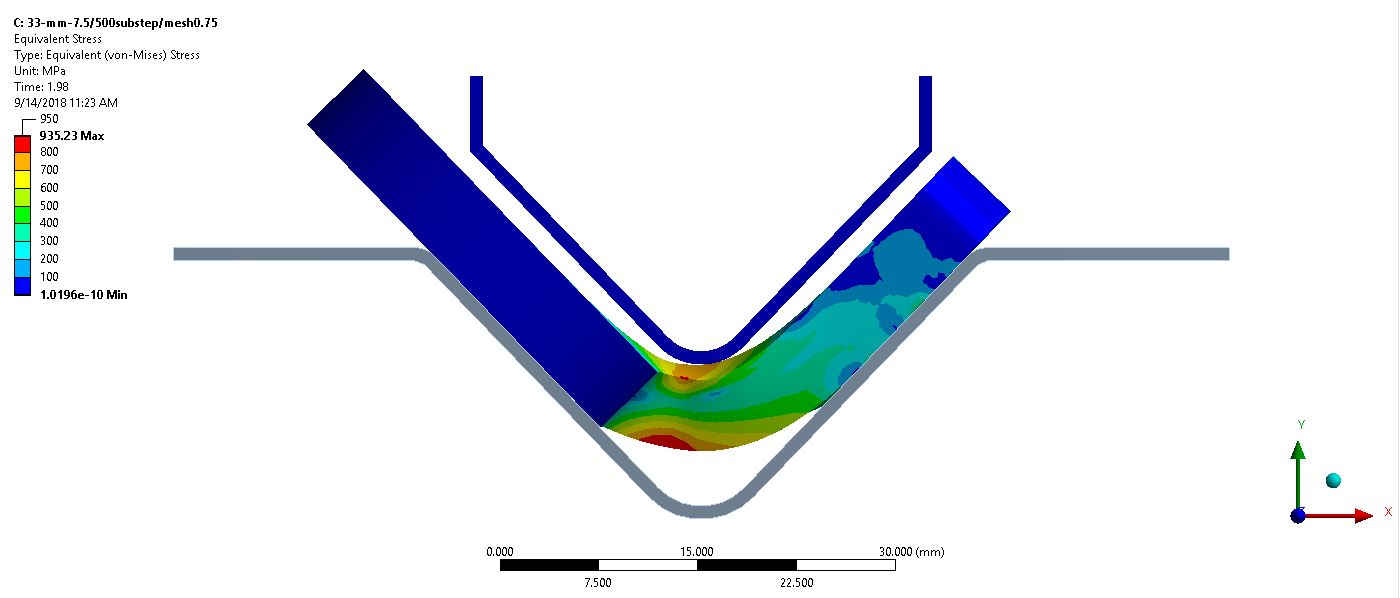
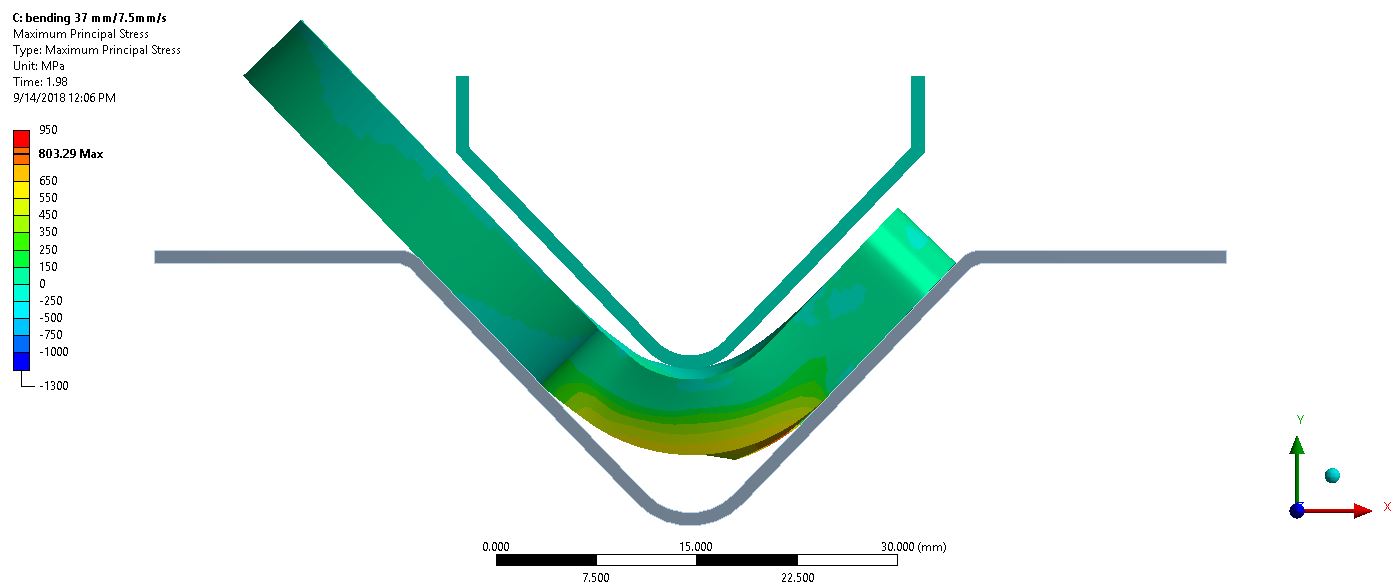
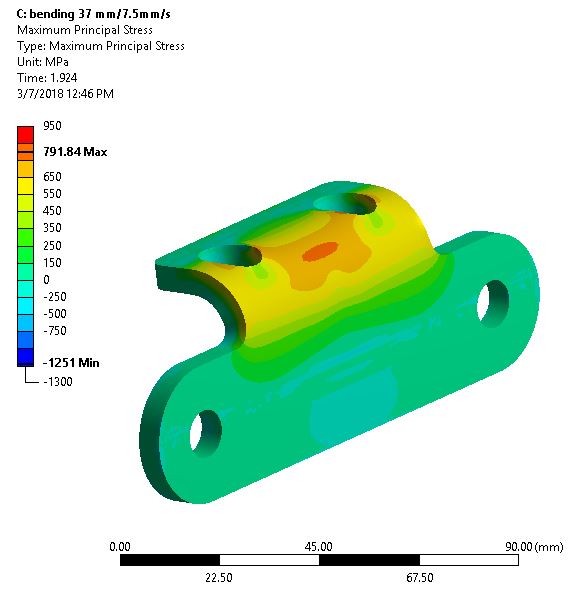
Thesis Title: A Comprehensive Analytical Overview of Wear Resistance and Mechanical Properties for the Longevity of Industrial Roller Chain Components
Publication: P. Thongjitr, P. Ninpetch, P. Kowitwarangkul, Wear Resistance Improvement of the Roller Chain Parts at Thai Metro Industry (1973) Co., Ltd., Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol, 5 No. 3 (2018): 9431–9439, DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.10.121
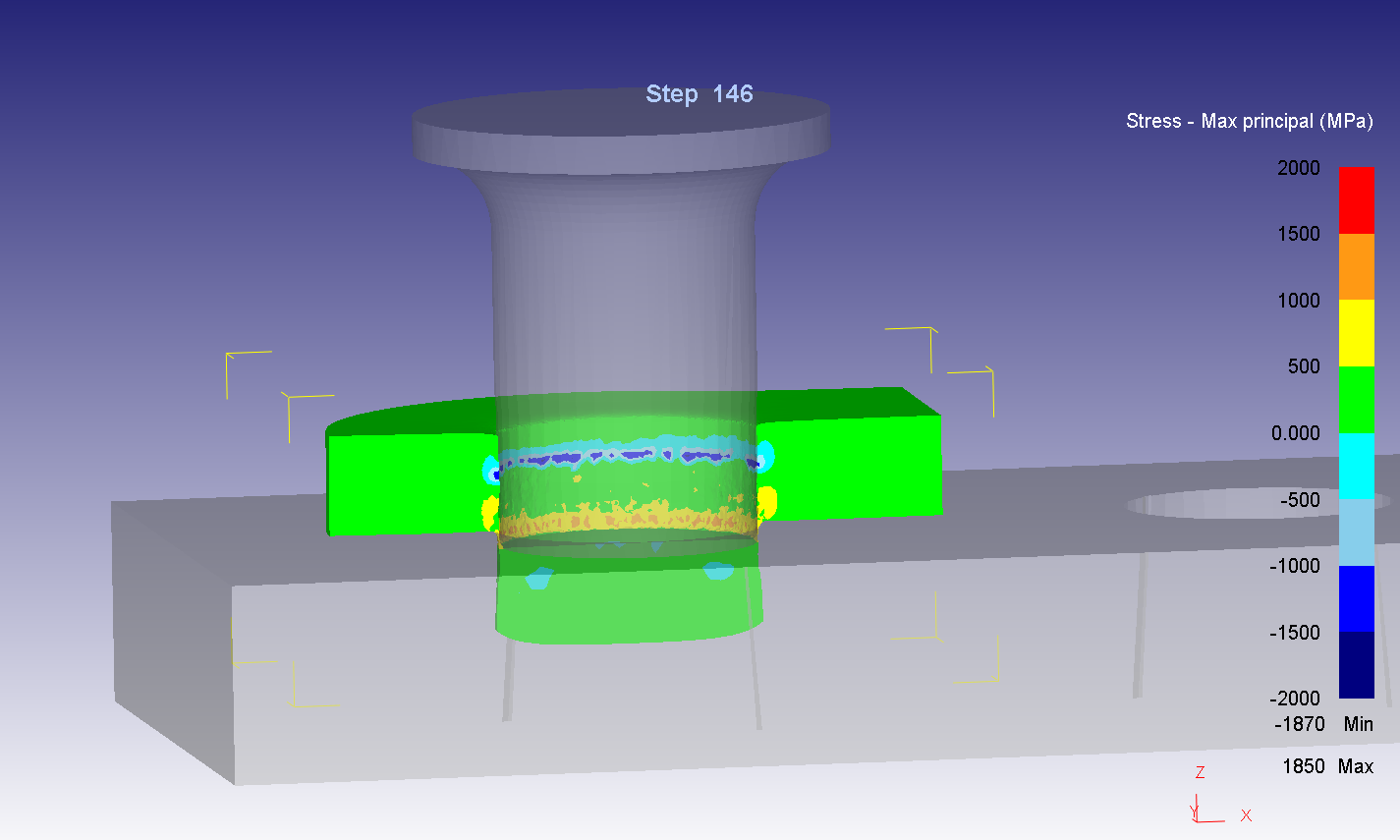
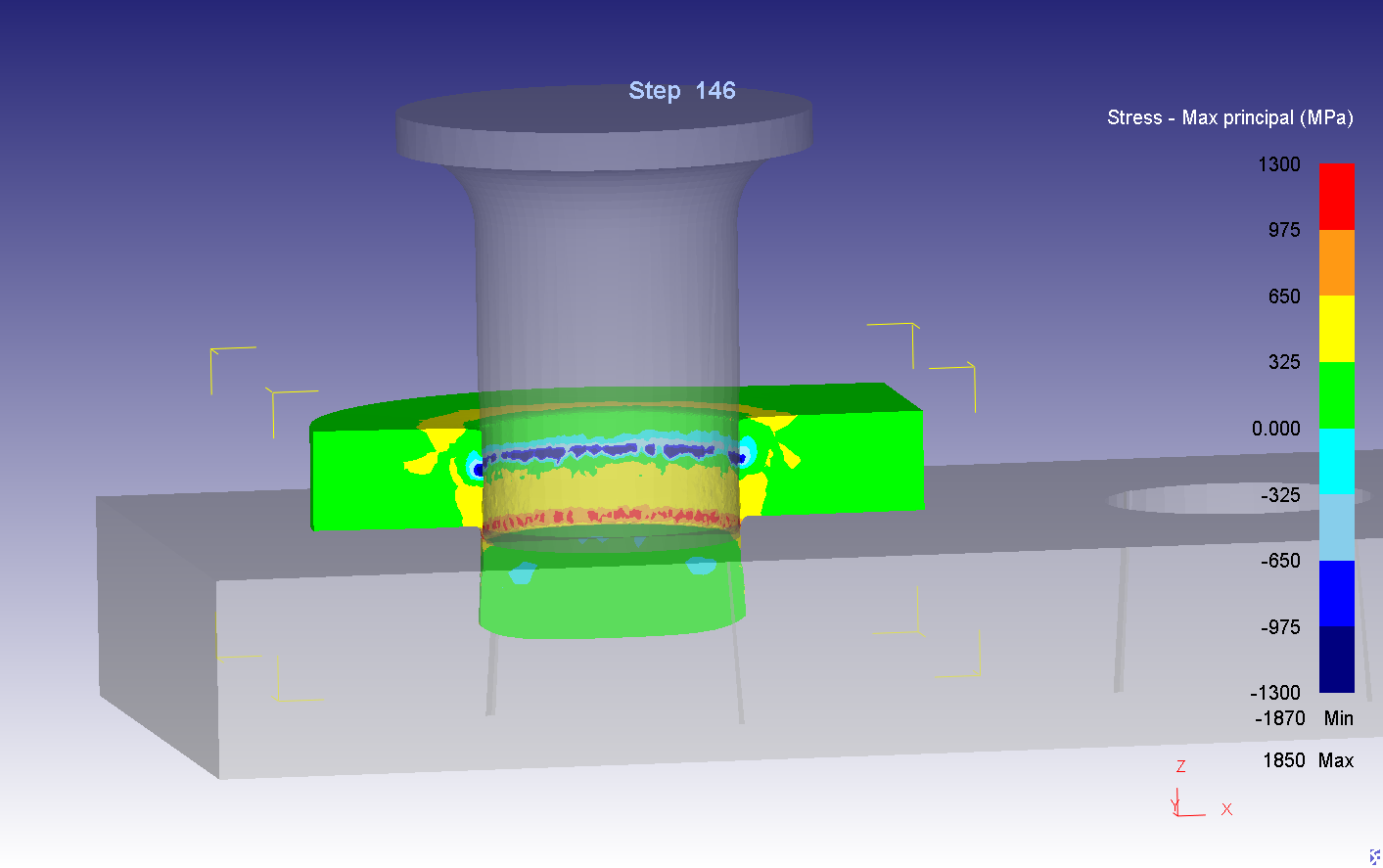
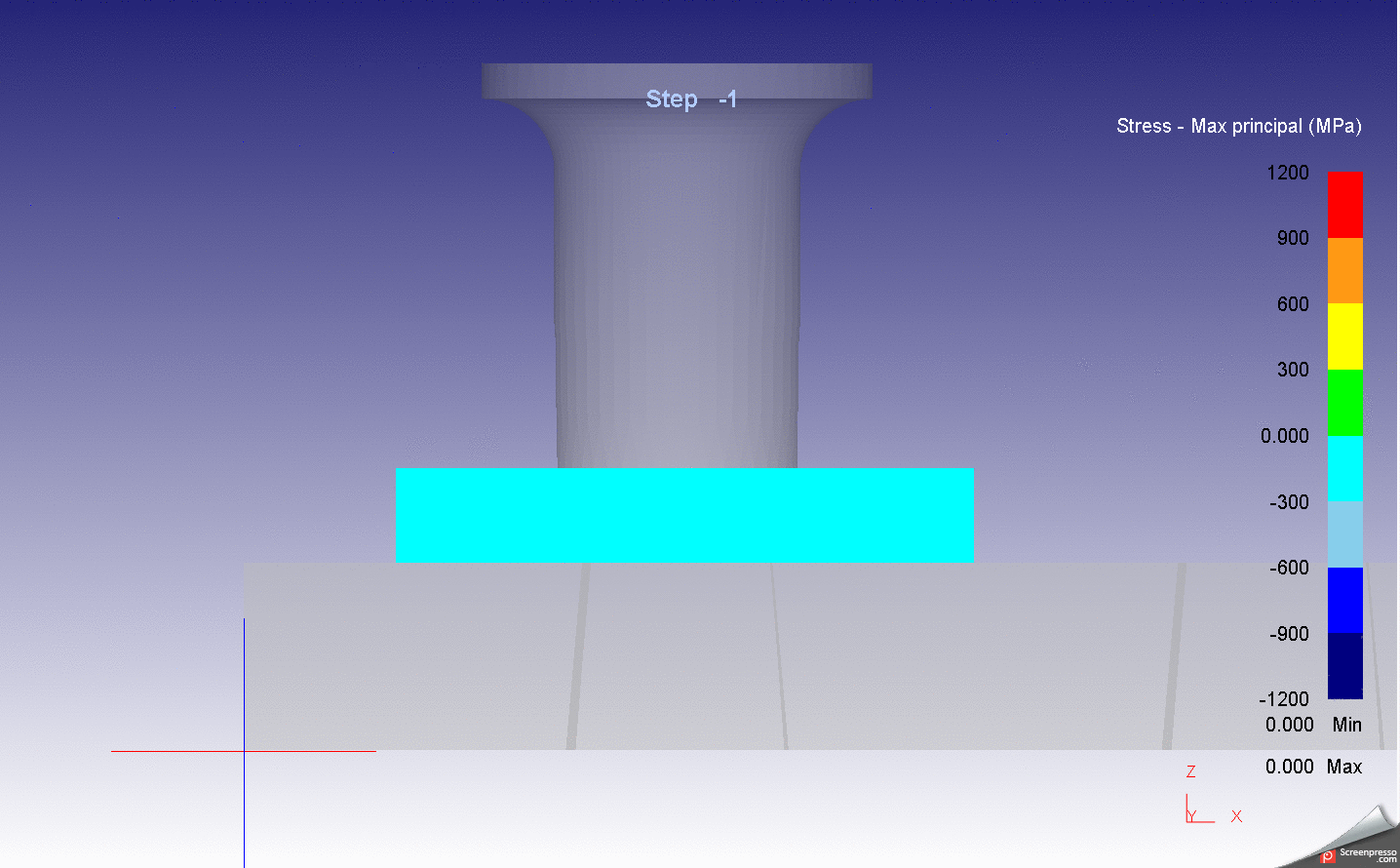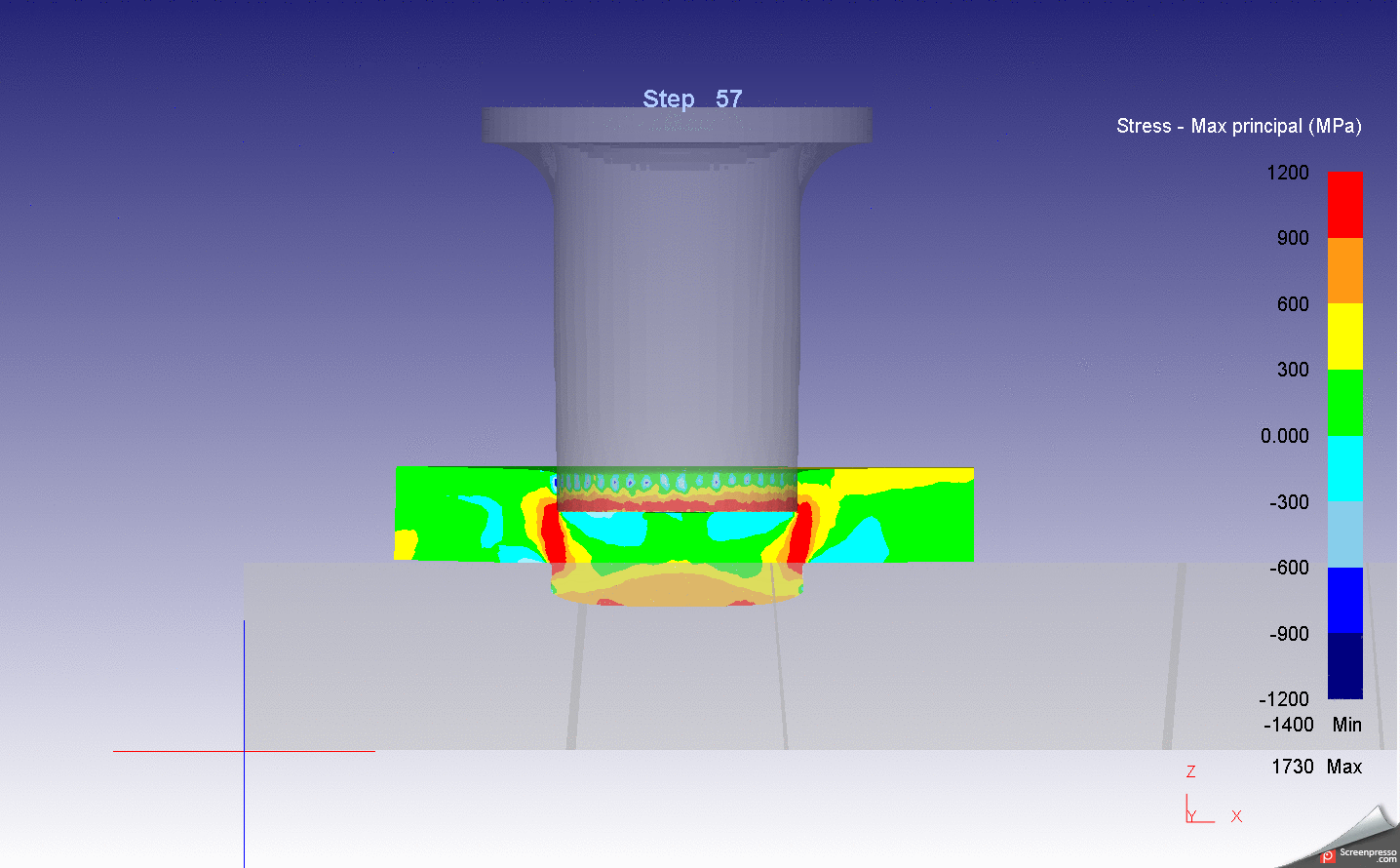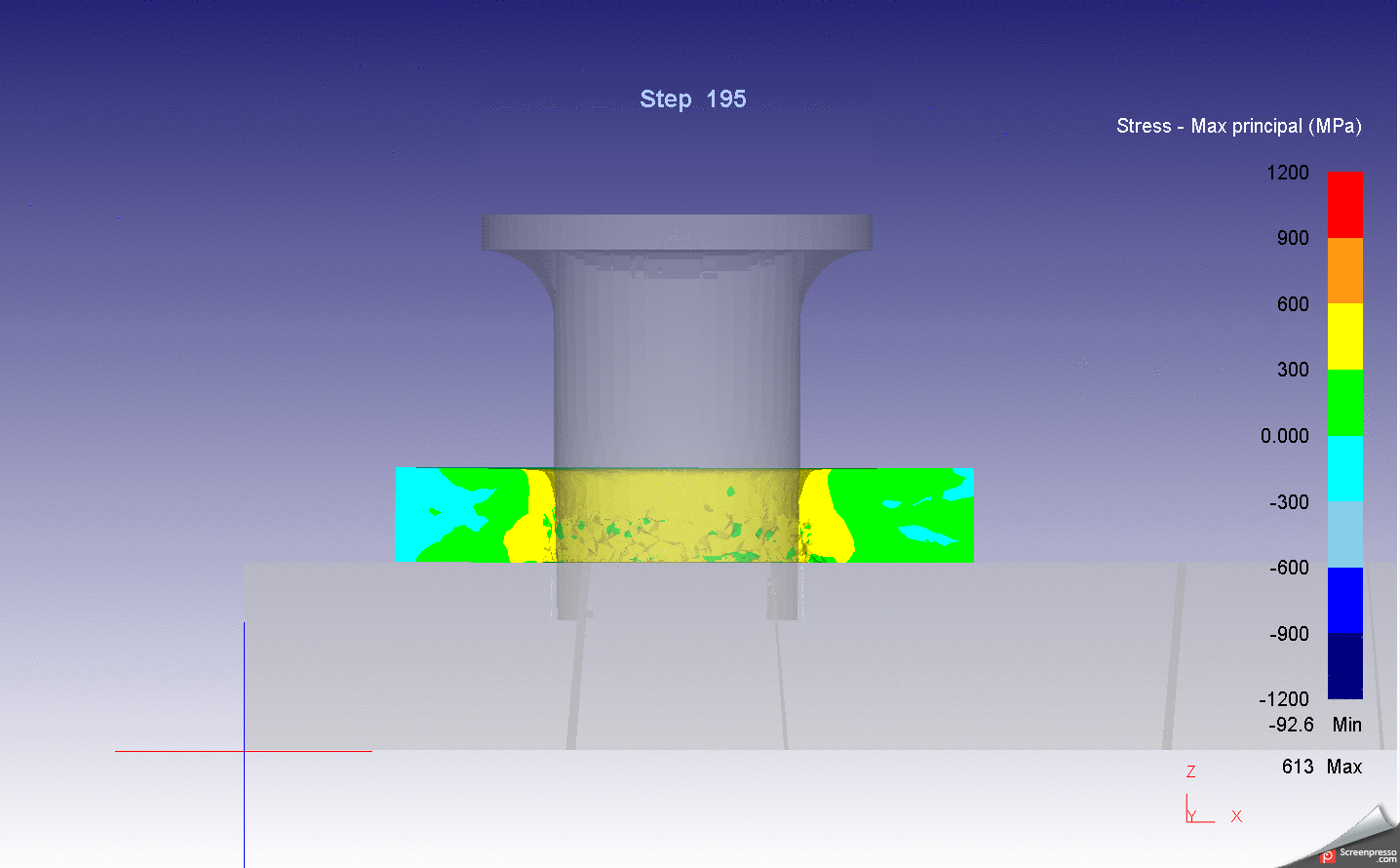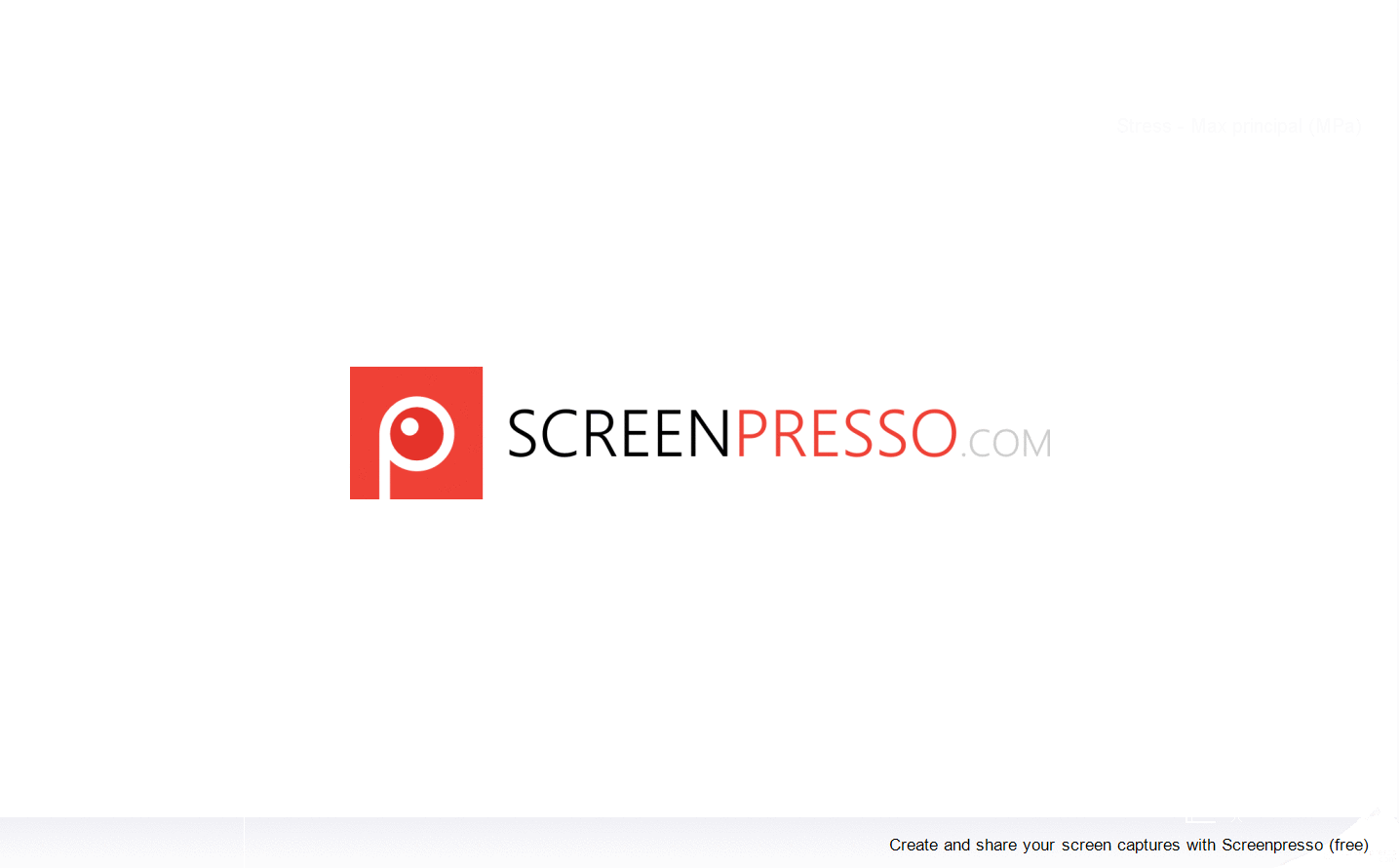
Abstract: This research aims to investigate and improve the surface hardness and wear resistance of the roller chain parts, which will result in the chain lifetime extension. The experiments were done by applying the carburizing and carbonitriding technique in the original heat treatment process of the example factory. The hardening media was charged into the industrial rotary retort furnace, which has a capacity of 60 kg/batch. The test samples are the roller chain parts, i.e. pin, bush which made from medium-carbon alloy steel with 0.4%C. The hardened specimens from the experiments were investigated by Micro Vickers hardness test, wear test, double shear test, Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) technique. The results show that the hardened specimens have better wear resistance property than the original product with an accepted shear strength and toughness.

Mr. Anawat Harnsihacacha

Thesis Title: CFD Simulation and Physical Water Modeling of the Flow in Continuous Casting Tundish
Degree: M.Eng
Publication:
1. A. Harnsihacacha, A. Piyapaneekoon, C. Wattanaporn, & P. Kowitwarangkul, Flow Prediction in The Multi-Strand Continuous Casting Tundish of Millcon Steel PLC., Materials Today: Proceedings, Vol. 5 No. 3 (2018): 9229–9237. DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.10.094
Abstract: The flow characteristics in the multi-strand continuous casting tundish of Millcon Steel PLC were investigated by CFD simulation and physical modelling. The aim of the study is to optimize the residence time distribution (RTD) which results in the better inclusion removal potential and the steel cleanliness. In this research, the 1:3 scale water model of the tundish was established. Tracer injections were computationally simulated using specie transport model and were physically simulated using red dye color mixed with sodium chloride. The flows are characterized by RTD curves which obtained from the tracer concentration measurement at the outlets. The results show that, among all outlets, the outlet in the middle position is critical and has very low of the minimum residence time. The flow modifiers can retard the minimum residence flow time and the mean residence time for all outlets which could promote the steel cleanliness.
2. A. Harnsihacacha, A. Piyapaneekoon, & P. Kowitwarangkul, Physical Water Model and CFD Studies of Fluid Flow in a Single Strand Tundish, Materials Today: Proceedings, 9220–9228, DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.10.093.
Abstract: Flow characteristics in a continuous casting tundish is one of the key parameters producing a high quality clean steel. In this study, the fluid flow analyses of a single-strand tundish model were carried out using the commercial CFD software ANSYS FLUENT 14.0 and experimentally verified by physical water model. The realizable k-ɛ equation was utilized to model turbulent phenomenon. The behavior and performance of the flow in tundish with and without flow modifiers were investigated by the residence time distribution (RTD) curves which were obtained from the tracer concentration measurement at the outlet. The results from CFD are in agreement with the experiment results. The results show that the flow modifier plays an important role in increasing residence time and enhancing flow performance which could feasibly promote the inclusion removal potentials in the tundish process. The peak and the minimum residence time of RTD curves of the tundish model with flow modifiers were improved for more than 20%. With the comparison of the four flow modifier configurations (bare tundish, dam, baffle and turbostop) in the current tundish model, it could be concluded that the turbostop could provide the optimal flow characteristic in which could improve the level of inclusion removable.
3. P. Kowitwarangkul, A. Harnsihacacha, Tracer Injection Simulations and RTD Analysis for the Flow in 3-Strands Steelmaking Tundish, Key Engineering Materials, Vol. 728 (2017): 72-77, DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.728.72
Abstract: Steel cleanliness in the continuous casting process can be improved by the enhancement of inclusion floatation via the flow control in tundish.The aim of this study is to define potential steel flow improvements in the 3-strands tundish of BSI (Bangkok Steel Industry) steelmaking shop. The numerical models of tundish without and with flow modifiers are simulated using the commercial computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software, ANSYS Fluent Workbench 14.0. The simulations of tracer injection using species transport model were performed. Flow characteristics were analyzed by RTD (residence time distribution) curves and the volumes fraction of three types of flow conditions. The results from this reseach shows how the current design of the flow modifiers improves some flow characteristics.